Deferred initiation of ART may increase risk for AIDS-defining cancer among patients living with HIV
Deferred antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation in ART-naive, HIV-positive persons is associated with a small increase in risk for AIDS-defining cancer. These findings add to the evidence that early ART may reduce risk for non-AIDS-defining cancer. A multinational prospective cohort study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Immediate initiation ART regardless of CD4 cell count has been recommended in all HIV-positive persons since 2015. However, only about half of HIV-positive persons in non-resource-limited settings continue to initiate ART when their CD4 count decreases below 500 cells/L, primarily because of late diagnosis. Incidence of non-AIDS-related and AIDS-related cancer is increasing in HIV-positive persons for a number of reasons and is now a leading cause of death in HIV infection. It is unclear to what extent delayed ART initiation, with its consequences of continued HIV replication and immune deterioration, contributes to the increased risk.
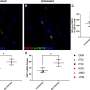
Researchers from University Hospital Basel and University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland studied data from D:A:D (Data collection on Adverse events of anti-HIV Drugs), a large observational database that included data from HIV-positive persons from Europe, Australia, and the United States, to estimate the 10-year risk difference for non-AIDS-defined and AIDS-defined cancer with two different ART initiation strategies—immediate or deferred. After adjusting for baseline and time-dependent confounders (CD4 cell count and viral load), the researchers found that the 10-year absolute risk of non-AIDS-defining cancer was slightly lower in the immediate ART group compared to the deferred treatment group. Strategies promoting deferral were associated with a small increase in risk for AIDS-defining cancer. More research is needed to determine the effect of early art on non-AIDS-defining cancer.
More information: Annals of Internal Medicine (2021). https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-5226