Gene changes might explain long-haul COVID-19 symptoms

Results from a new cell study suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein can bring about long-term gene expression changes. The findings could help explain why some COVID-19 patients—referred to as COVID long-haulers—experience symptoms such as shortness of breath and dizziness long after clearing the infection.
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is covered in tiny spike proteins. During infection, the spike proteins bind with receptors on cells in our body, starting a process that allows the virus to release its genetic material into the inside of the healthy cell.
"We found that exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone was enough to change baseline gene expression in airway cells," said Nicholas Evans, a master's student in the laboratory of Sharilyn Almodovar, Ph.D., at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center. "This suggests that symptoms seen in patients may initially result from the spike protein interacting with the cells directly."
Evans will present the research at the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meeting during the virtual Experimental Biology (EB) 2021 meeting, to be held April 27-30.
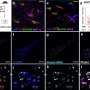
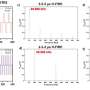
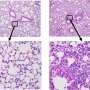
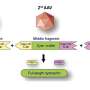
Culturing human airway cells requires specific conditions that allow cells to mature into the differentiated cells that would be found in the airway. The researchers optimized a previously developed culturing approach known as the air-liquid interface technique so that it would more closely simulate the physiological conditions found in the lung airway. This involved exposing cells to air and then giving them time to mature into airway cells.

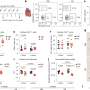
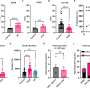
The researchers found that cultured human airway cells exposed to both low and high concentrations of purified spike protein showed differences in gene expression that remained even after the cells recovered from the exposure. The top genes included ones related to inflammatory response.
"Our work helps to elucidate changes occurring in patients on the genetic level, which could eventually provide insight into which treatments would work best for specific patients," said Evans.
The researchers also compared their cultured human airway cells to studies from others where cells were collected from patients with COVID-19 infection. They were able to confirm that the optimized cell culture approach reflected what occurs in patients, making it useful for future translational studies. They plan to use the new approach to better understand how long the genetic changes last and the potential long-term consequences of these changes in relation to long-haul COVID-19 cases.
More information: Nicholas Evans will present the findings from 12:00-12:15 p.m. Friday, April 30 (abstract).