Study reveals how Y-box binding protein 1 promotes cancer metastasis
Metastasis of cancer is the main cause of cancer relevant death as well as the main challenge of cancer treatment.
Recently, a group led by Prof. Piao Hailong from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) revealed that the nucleotide binding protein Y-box binding protein 1 (YB1) can promote the metastasis of liver cancer by regulating the biosynthesis of microRNA (miRNA).
This study was published in Cancer Communications on June 10.
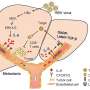
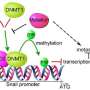
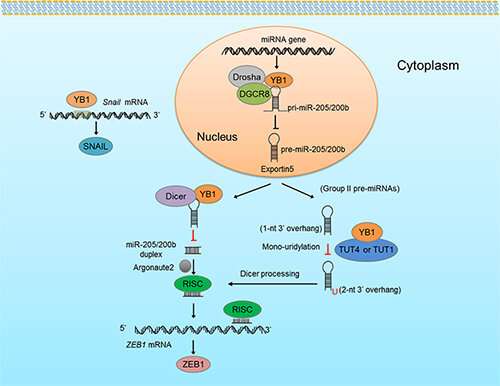
The researchers found that YB1 could significantly inhibit the biosynthesis and expression of miRNA-200b and miRNA-205 by interacting with miRNA microprocessor complex DgCR8, Dicer and terminal UTP transferase TUTs. Then, it up-regulated the expression of zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), which is a key protein for cancer metastasis.
The development of lung cancer metastasis was simulated by a mouse model injected through tail vein, and the researchers found that YB1 could promote lung metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Furthermore, transcriptomics data of clinical tissues showed that the expression of YB1 was positively correlated with ZEB1 in liver cancer tissues, and negatively correlated with the expression of miRNA200 and miRNA205b. The miRNA200/205b-ZEB1 signaling pathway was significantly correlated with the prognosis of patients.
More information: Xiumei Liu et al, YB1 regulates miR‐205/200b‐ ZEB1 axis by inhibiting microRNA maturation in hepatocellular carcinoma, Cancer Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12164