Community support can make you healthier—and can help you lose weight, too
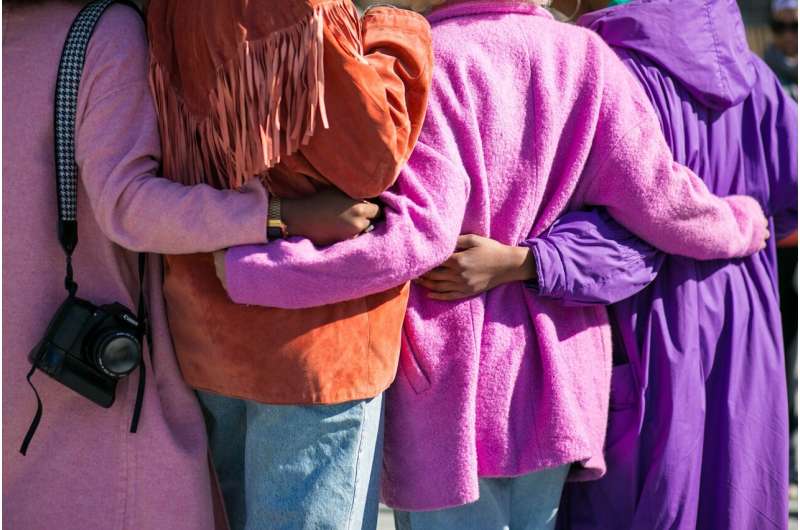

During the COVID-19 pandemic, many people's lives were disrupted, and isolation increased. And with that isolation came weight gain.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says children and adults have gained weight during the pandemic, stressing that obesity worsens COVID-19 outcomes. However, a recent Mayo Clinic community-based pilot study suggests that weight gain can be prevented and perhaps reversed—even during a pandemic—with the help and support of a person's community.
The pilot study examined the feasibility and acceptability of a 12-week behavioral program for weight loss and improved cardiovascular health. It was designed to be used with Somali and Hispanic immigrants living in Southeast Minnesota. The peer-led intervention was delivered by community-based "health promoters."
Despite the challenges of the pandemic, the study retained 100% of its participants. They rated the intervention highly, as they lost weight, lowered their blood pressure and improved health behaviors. The researchers are part of the Rochester Healthy Community Partnership, a community-academic research program in Rochester that was formed in 2004.
"Participants lost 2% of their body weight on average while significantly reducing blood pressure, increasing physical activity and improving dietary quality," says Mark Wieland, M.D., a community internal medicine physician at Mayo Clinic and first author of the study.
The study, which launched just before the pandemic began, initially set out to help participants lose 3% of their body weight. Despite the effects of the pandemic, the authors note that participants in their study still achieved weight loss, along with significant improvements in other cardiovascular health measures.
"It was a difficult time, and the fact that people stuck with the program and succeeded despite the unexpected challenges speaks to the power of social networks to promote healthy behaviors and healthy communities," says Dr. Wieland.
The researchers indicate the peer-led, community-based model contributed to the success of the intervention. Research participants agreed, saying the role of lay health promoters was key.
"Speaking the same language and being able to understand us―you see that is the biggest thing. When someone (a health promoter) knows your lifestyle, your community, your language, then they understand your culture," said one of the study's participants. The participant's name was redacted in the study.
The researchers note that immigrants often arrive to the U.S. at a healthier weight than the general population, but these advantages disappear over time. Past research suggests that culturally tailored interventions are needed. In this study, the authors assert that community-academic partnerships like the Rochester Healthy Community Partnership are ideally positioned to carry out this work.
"When community and academic members partner equitably in all phases of research and intervention development, that enhances the relevance of health promotion by addressing the roots of health behaviors in culturally relevant ways," says Irene Sia, M.D., a Mayo Clinic infectious diseases physician and senior author on the paper.
Further study is needed. The community and academic partners have begun a randomized clinical trial as a next step in this research.
The research was published in American Journal of Health Promotion.
More information: Mark L. Wieland et al, Pilot Social Network Weight Loss Intervention With Two Immigrant Populations During the COVID-19 Pandemic, American Journal of Health Promotion (2022). DOI: 10.1177/08901171211053450