Researchers find humans have given wild animals their diseases nearly 100 times
A research team led by scientists at Georgetown University has found that humans give viruses back to animals more often than previously thought.
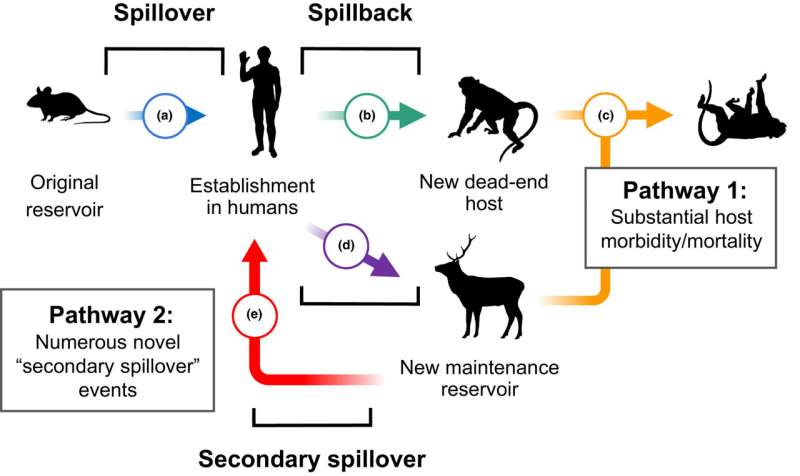
In a study published in Ecology Letters, the authors describe nearly 100 different cases where diseases have undergone "spillback" from humans to wild animals, much like how SARS-CoV-2 has spread in mink farms, lions and tigers in zoos, and wild white-tailed deer.
"There has understandably been an enormous amount of interest in human-to-wild animal pathogen transmission in light of the pandemic," said Gregory Albery at Georgetown University, the study's senior author.
The new study is part of a U.S. National Science Foundation-funded project called The Viral Emergence Research Initiative, or Verena. The Verena team uses data science and machine learning to study the science of the host-virus network—a new field that aims to predict which viruses can infect humans, which animals host them and where, and when and why they might emerge.
"Disease transmission, where it comes from and where it goes, can be much more complicated than we often consider," says Sam Scheiner, a program director in NSF's Division of Environmental Biology. "This project is an important step in sorting out that complexity."
Albery and colleagues found that almost half the incidents identified occurred in captive settings like zoos, where veterinarians keep a close eye on animals' health and are more likely to notice when a virus makes the jump. More than half the cases they found were human-to-primate transmission, an unsurprising result because pathogens find it easier to jump between closely related hosts, and because populations of endangered great apes are so carefully monitored.
"We're more likely to detect pathogens in the places where we spend a lot of time and effort looking, with a disproportionate number of studies focusing on charismatic animals at zoos or in close proximity to humans" said Anna Fagre, a virologist and wildlife veterinarian at Colorado State University, who was lead author on the study. "It brings into question which cross-species transmission events we may be missing, and what this might mean not only for public health, but for the health and conservation of the species being infected."
Disease spillback has recently attracted substantial attention due to the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in wild white-tailed deer in the U.S. and Canada. Many scientists have expressed concerns that new animal reservoirs might give the virus extra chances to evolve new variants. In the study, Albery and colleagues found a sliver of good news: Scientists can use artificial intelligence to anticipate which species might be at risk of contracting the virus.
More information: Anna C. Fagre et al, Assessing the risk of human‐to‐wildlife pathogen transmission for conservation and public health, Ecology Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1111/ele.14003