Vaccine use in pregnancy: Deferring risk

Existing gaps and serious limitations concerning the information in vaccine product labels makes it challenging for health care providers to know when to recommend vaccination to pregnant women. A new study, which identified these knowledge gaps, surveyed health care providers, and recommended improvements for the future is published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health.
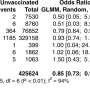
Health care providers are often hesitant to recommend vaccination in pregnancy, and this hesitancy has been linked to inconsistencies and ambiguity in vaccine information, evidence, and policies, including information in vaccine labels. In their survey, Janice Graham, Ph.D., from Dalhousie University and the Canadian Center for Vaccinology, and coauthors, showed that health care providers were uncertain about the purpose of vaccine product labels and the evidence contained in them. More than a third of the survey respondents incorrectly thought that the information contained in the product labels was updated regularly. "Most health care providers were unaware that labels are not up-to-date about the risks or burden of the disease," state the investigators.
"More frequent updating and alignment of robust, unbiased, and independently reviewed clinical trial and post-market safety and effectiveness evidence with Nation Immunization Technical Advisory Group recommendations would allay health care providers and public misunderstanding," conclude the investigators.
"For the COVID-19 vaccines, specifically, there are no data about pregnancy and breastfeeding included in the labeling. As noted by the authors, despite the growing body of evidence about the use of COVID-19 vaccines and the risk of severe disease from COVID-19, there is no indication if/when those vaccine labels will be updated," says Journal of Women's Health Editor-in-Chief Susan G. Kornstein, MD, Executive Director of the Virginia Commonwealth University Institute for Women's Health, Richmond, VA.
More information: Terra Anne Manca et al, Deferring Risk: Limitations to the Evidence in Product Labels for Vaccine Use in Pregnancy, Journal of Women's Health (2022). DOI: 10.1089/jwh.2021.0609