Trust in health care is essential for dealing with antibiotic resistance
Do many Swedes obtain antibiotics without a prescription, and what drives their behavior when this happens? The answers are important when it comes to dealing with antibiotic resistance, which is a serious challenge for the entire health care sector. Practical philosophers and political scientists at the University of Gothenburg have carried out a large study examining Swedes' experiences of—and attitudes towards—obtaining antibiotics without a prescription.
The researchers are affiliated with the Center for Antibiotic Resistance Research (CARe) at the University of Gothenburg, and their study has recently been published in PLOS One.
In order to slow down the development of resistant bacteria it is key to limit the use of antibiotics. This is why health care services are trying to limit prescriptions for antibiotics, with doctors being encouraged to take a restrictive approach. At the same time, there are many opportunities to get hold of antibiotics without a prescription, such as when traveling abroad, via foreign contacts or from online pharmacies that circumvent national regulations.
"First we conducted a smaller pilot study," says Christian Munthe, who led the study in collaboration with Erik Malmqvist and Björn Rönnerstrand. "Eighteen percent of respondents indicated that they had obtained antibiotics without a prescription and 16 percent would consider doing so, which was highly concerning. Their motivation was often that they were unhappy with or did not trust health care."
Few research studies
The researchers only found a few publications on the subject, most of which dealt with related phenomena or pharmaceuticals in general. However, no study had examined the issue specifically for antibiotics, or why some people circumvent society's rules that are intended to control antibiotic use.
"We therefore went ahead with a large study using the SOM Institute's Swedish Citizen Panel, with several thousand people who make up a more representative sample of the population as a whole, enabling us to examine the hypothesis that trust in health care plays an important role in this phenomenon," explains Christian.
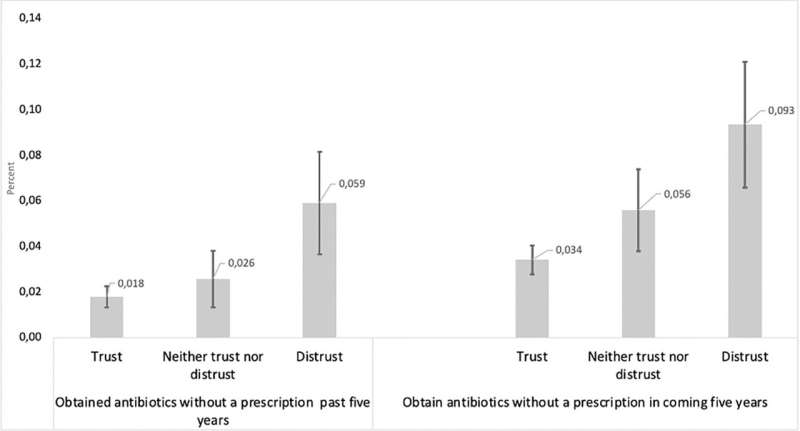
One of their main findings was that the proportion of Swedes who have obtained or want to obtain antibiotics without a prescription is lower than the pilot study suggested. At the same time, almost twice as many—just under 5 percent of the respondents—would be willing to do so in the future compared to those who reported having done so (2.3 percent). The other main finding is that trust in health care—or lack of trust—outweighed all other potential explanatory factors, such as level of education and concerns about one's own health.
Action needed
"Because we know that trust in health care varies widely from country to country, our results provide a strong reason for countries with trust rates that are lower than the Nordic countries to review the situation and put measures in place if it turns out that many people are obtaining antibiotics without prescriptions."
The researchers believe that Sweden also has good reason to monitor this issue in view of how many people are prepared to buy antibiotics without prescriptions in the future.
"It is also important to consider the need to maintain and strengthen trust in health care when devising strategies to limit antibiotic use."
More information: Christian Munthe et al, Non-prescription acquisition of antibiotics: Prevalence, motives, pathways and explanatory factors in the Swedish population, PLOS ONE (2022). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273117