Genetic lineage tracing identifies cardiac mesenchymal-to-adipose transition in an arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy model
ACM is a hereditary cardiomyopathy characterized by fibrofatty replacement of the ventricular myocardium, a high risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, sudden cardiac death, and progressive heart failure. However, the cellular origin of cardiac adipocytes in ACM remains largely unknown.
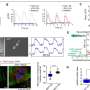
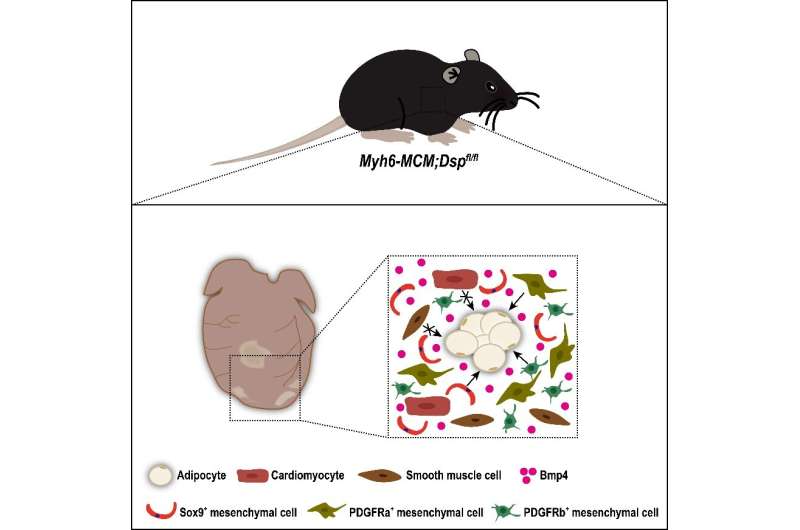
In a study recently published in Science China Life Sciences, a research team established an ACM mouse model using the inducible Myh6-MerCreMer (Myh6-MCM) to delete the floxed Dsp gene (Dspfl) specifically in cardiomyocytes. Sirius red and Oil Red O staining showed obvious fibrosis and adipocyte accumulation in the ACM mouse hearts.
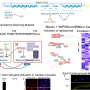
Echocardiographic analyses also demonstrated deteriorated heart function of the ACM mice. Then, researchers studied the adipogenic potential of cardiomyocytes and mesenchymal cells in the model. First, they crossed the Myh6-MCM;Dspfl/flmice with a reporter line Rosa26-loxp-stop-loxp-tdTomato (R26-tdT) to investigate the contribution of cardiomyocytes to adipocytes in the ACM mouse hearts.
It was found that cardiomyocytes did not give rise to cardiac adipocytes in the model. Next, researchers examined the contribution of mesenchymal cells to cardiac adipocytes in the model by employing various mouse tools, which can target different mesenchymal subpopulations (e.g., fibroblasts, vascular pericytes and smooth muscle cells) in mouse hearts.
It was found that the SOX9+, PDGFRa+ and PDGFRb+ mesenchymal cell populations, but not smooth muscle cells, gave rise to cardiac adipocytes in the ACM model. Furthermore, the researchers found that Bmp4 was highly enriched in the ventricles of the ACM mouse hearts and might participate in promoting cardiac mesenchymal-to-adipose transition in the model.
This study clarifies the cellular origin of cardiac adipocytes in an ACM model and provides in-depth insights into understanding the pathogenesis and adipogenesis of ACM.
More information: Xinyan Huang et al, Genetic lineage tracing identifies cardiac mesenchymal-to-adipose transition in an arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy model, Science China Life Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11427-022-2176-6