This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Most babies born to mothers with COVID-19 were separated after birth, resulting in low breastfeeding rates
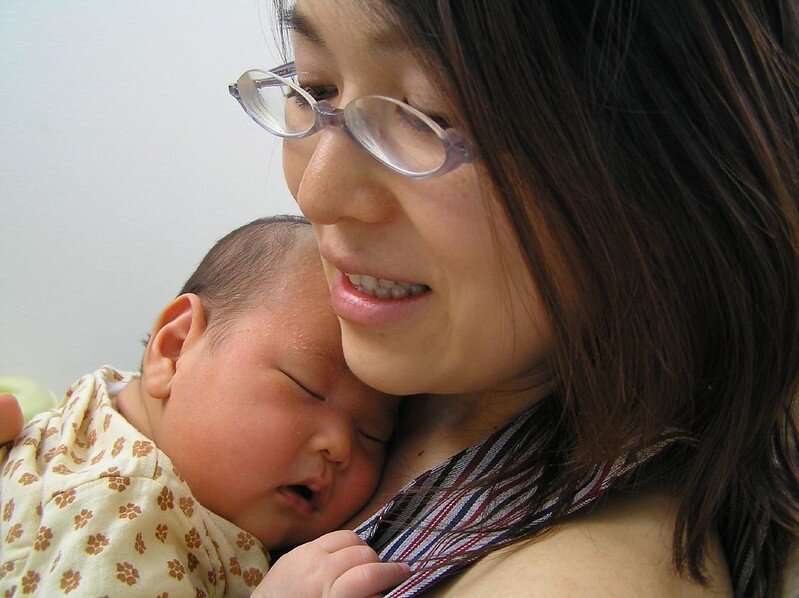

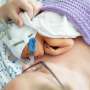
Most babies born to mothers with COVID-19 were separated after birth resulting in low breastfeeding and skin-to-skin contact rates during the height of the pandemic, according to a new global study.
The international research, led by Murdoch Children's Research Institute in collaboration with the the European Society of Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC), found that transmission of COVID-19 from mother to baby was rare and generally mild when it occurred. But despite this, almost half of all babies did not receive any breast milk, with only a quarter being breastfed and the majority of mothers and babies having no skin-to-skin contact immediately after birth.
Murdoch Children's Professor David Tingay said the study, the largest on global family-centered care during COVID-19, highlighted how ensuring good infection control measures had significantly impacted neonatal practice over the past few years.
"Almost half of all newborns in the trial were denied early and close contact with their mother, demonstrating how hard it was to balance infection control measures with mother-baby bonding recommendations, especially in the first year of the pandemic," he said. "Encouragingly, clinicians did gradually adapt to allow more family-centered care as the pandemic progressed, particularly the use of breastmilk."
The study, published in eClinicalMedicine, involved 692 babies born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 in 13 neonatal intensive care units across 10 countries , including Brazil, France, Italy and the US, who participated in the EPICENTRE trial.
It found 54 percent of newborns were separated from their mother and only 7 percent had physical contact before separation. Maternal breastmilk feeding rates were low at 53 percent, with just 24 percent exclusively fed with their mother's breastmilk. But contact and breastfeeding increased over time from 23 percent in Spring 2020 to 70 percent in Winter 2020/21 (northern hemisphere seasons).
Additionally, 73 percent of those separated from their mother were admitted into a neonatal intensive care unit or special care nursery without any symptomatic or underlying condition to account for admission. Only 5 percent of babies born to infected mothers tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and most cases were mild.
Murdoch Children's Dr. Georgie Dowse said the benefits of family-centered care in the perinatal period for both mothers and babies were well-established.
"Family-centered care practices such as breastfeeding, co-habitation and skin-to-skin contact are critical to the well-being of mothers and neonates, even those needing intensive care," she said.
"Breastmilk provides a baby with nutrition and supports growth and development. Breastfeeding can help protect baby and mother against certain illnesses and diseases spanning asthma, obesity, type 1 diabetes and sudden infant death syndrome. Skin-to-skin contact helps babies adjust to life outside the womb and supports mothers to initiate breastfeeding and develop close, loving relationships with their baby."
Professor Tingay said the impact of COVID-19 on family-centered care should be considered when updating infection control guidelines.
"The COVID-19 pandemic has created unprecedented challenges for healthcare services, including the delivery of family-centered care," he said. Guidelines for the management of neonates born to infected mothers were initially formulated in the context of many unknowns and often varied and based on expert consensus rather than evidence.
"An encouraging finding was the increased provision of family-centered care practices as the pandemic progressed, even when the mother was very sick herself. We are hopeful doctors and nurses will use the experiences from the pandemic to better family-centered care whenever a mother or baby is unwell.
"We strongly encourage health services to continue implementing family-centered care practices during the future stages of this pandemic to ensure neonates and mothers receive the best possible health benefits."
More information: Born into an Isolating World: Family-Centred Care for Babies Born to Mothers with COVID-19 The EPICENTRE Multinational Cohort Study, eClinicalMedicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101822