This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Finding a way to combat long COVID
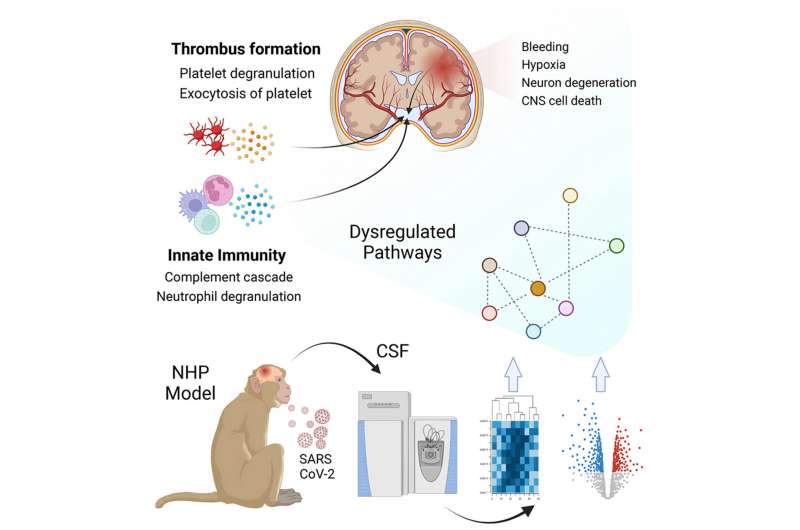
A new study has identified potential neurological biomarkers of long COVID-19 in nonhuman primates that may help physicians diagnose, monitor and treat this condition.
Over 65 million people worldwide have developed long COVID after being infected with SARS-CoV-2, and cases are only becoming more common. Long COVID symptoms can last weeks, months or years.
Even more perplexing is the fact that symptoms can vary widely between individuals and consist of any combination of fatigue, fever, chest pain, trouble breathing, neurological symptoms such as "brain fog," and many more. Long COVID puts a gigantic burden on the U.S. healthcare system, and some doctors doubt the condition exists, leaving some patients unable to find care.
A team of researchers at Tulane University is trying to shed light on this condition and find tools to manage it. They published their work in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
"Our primary goal was to better understand the inside of the brain after COVID infection," said Jia Fan, an assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology who oversaw the study. "This understanding could provide a potential target to use in the clinic for long COVID evaluation and monitoring. We also thought this study may give us some clues to find a potential treatment strategy for long COVID in patients."
However, because long COVID can vary drastically between individuals, studying this disorder has been difficult for scientists and clinicians alike.
"There's a very limited understanding of the neuropathogenesis of long COVID," Fan said. "It is almost impossible to get any brain tissue or samples of any kind from patients that have mild symptoms or no long COVID symptoms because there is no reason for invasive procedures."
Therefore, the group turned to a nonhuman primate model of long COVID.
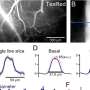
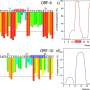
The team found that certain proteins associated with neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, were elevated in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid and blood after SARS-CoV-2 infection even in nonhuman primates that showed mild or no symptoms. Maity explained that these elevated proteins indicate that the immune systems of the monkeys remained activated even after infection.
"Our findings suggest that the major neurological complications are arising due to the body's natural immune defenses," Maity said. "The immune system has a very important and significant impact on the neurological complications of COVID."
The next steps of the project involve validating the biomarkers the team identified in human samples such as blood, said Fan.
"It is currently hard to score the severity of (long COVID) patient symptoms because they are based on self-reports," Fan said. "If we can find a group of proteins in the blood associated with long COVID, this is a less invasive way to easily evaluate the severity of the long COVID patients. We hope what we started can provide a clue to find a potential treatment to better the long COVID patient experience."
More information: Sudipa Maity et al, Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein Markers Indicate Neuro-Damage in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Nonhuman Primates, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100523