This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Artificial intelligence can help categorize and triage primary care patients with respiratory symptoms
Researchers from Iceland trained a machine learning model with artificial intelligence to triage patients with respiratory symptoms before the patients visit a primary care clinic.
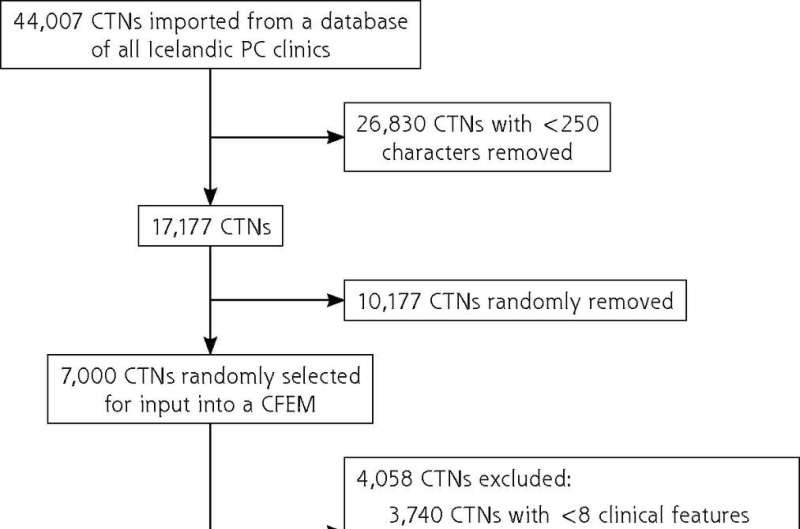
To train the machine learning model, the researchers used only questions that a patient might be asked about before a clinic visit. Information was extracted from 1,500 clinical text notes that included a physician's interpretation of the patient's symptoms and signs, as well as reasons for clinical decisions made during the consultation, such as imaging referrals and prescriptions.
Patients were categorized into one of five diagnostic categories based on information in clinical notes. Patients from all primary care clinics in the capital area of Iceland were included. The model scored each patient in two extrinsic datasets and divided patients into 10 risk groups. The researchers then analyzed selected outcomes in each group.
Patients in risk groups 1-5 were younger, had lower rates of lung inflammation, were less likely to be re-evaluated in primary and emergency care, were less likely to receive antibiotic prescriptions or chest X-ray referrals, as compared to higher risk groups 6-10. The lowest five groups contained no chest X-rays with signs of pneumonia or a pneumonia diagnosis by a physician. Researchers concluded that the model can reduce the number of chest X-ray referrals by eliminating them in risk groups 1-5.
What we know:
Respiratory symptoms are common reasons people visit primary care clinicians . However, many of their symptoms are self-resolving. Researchers argue that triaging patients before physician consultations may reduce unnecessary diagnostic testing; health care costs; and overprescription of antibiotics, which can lead to greater bacterial resistance.
What this study adds:
Researchers found that a machine learning model can effectively categorize patients among 10 risk groups, allowing clinicians to communicate with lower-risk patients in ways that don't add to their heavy work schedule and can allow for them to care for higher-risk patients and those with severe respiratory symptoms. The team asserts that the machine learning model could reduce costs for patients, the health care system, and society.
The research is published in The Annals of Family Medicine journal.
More information: Steindór Ellertsson et al, Triaging Patients With Artificial Intelligence for Respiratory Symptoms in Primary Care to Improve Patient Outcomes: A Retrospective Diagnostic Accuracy Study, The Annals of Family Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1370/afm.2970