This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Language barriers found to negatively affect clinical outcomes
Faculty from the University of Minnesota and HealthPartners Institute recently published an analysis in JAMA Network Open on the first large-scale study in the U.S. to demonstrate that a patient's language and need for an interpreter are associated with clinical outcomes.
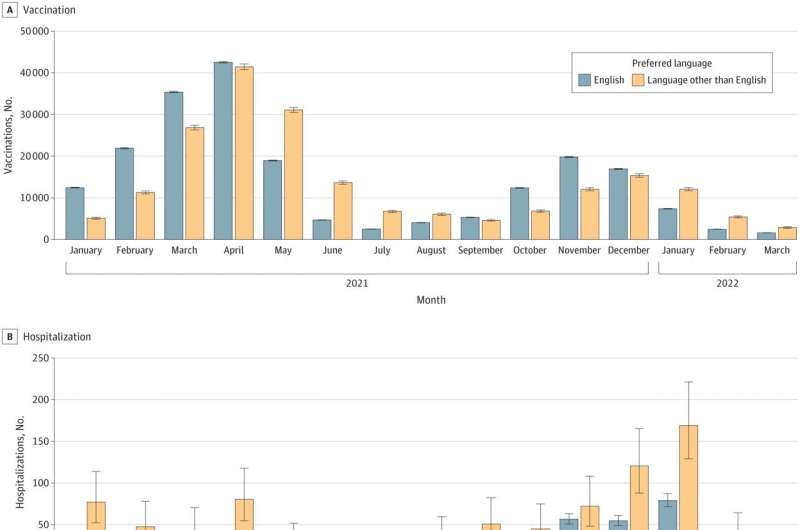
The analysis found patients with a language preference other than English (LPOE) and those with limited English proficiency (LEP), as measured by interpreter need, were more likely to experience delays in COVID-19 vaccination and become hospitalized and/or die from COVID-19 compared to their peers who primarily speak English.
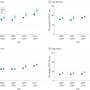
The team analyzed COVID-19 vaccine uptake rates and associated hospitalizations and deaths from December 2020 to March 2022 in a large health care system in Minnesota and Wisconsin that serves a uniquely multilingual population.
Key findings from the analysis include:
- Patients with LPOE and LEP experienced delays in receiving their first vaccine dose and increased rates of COVID-19–associated hospitalization and death.
- Patients with LPOE and LEP were approximately twice as likely to be hospitalized or die due to COVID-19 than English-speaking patients.
- Delayed time to vaccine and worse health outcomes patterns suggest patients with LPOE or LEP is a crucial risk factor influencing health disparities.
"This study suggests that routine data collection of a patient's preferred language and interpreter needs should be standard of practice and could provide key information on improving health equity in the U.S.," said William Stauffer, MD, a professor at the U of M Medical School and director of Human Migration and Health at the Center for Global Health and Social Responsibility.
Although racial and ethnic categories remain the most common method for describing U.S. health disparities, they provide minimal direct intervention information. Further analysis of language preference can increase local knowledge to identify social groups for engaging trusted messengers, forging community partnerships, developing culturally appropriate interventions and delivering messages in an acceptable, linguistically congruent medium.
"In a health care setting, language is more than a communication tool. It conveys respect, upholds a patient's dignity, and gives patients autonomy over their care," said lead author Nasreen Quadri, MD, an adjunct assistant professor affiliated with the U of M Medical School and physician collaborator with the National Resource Center for Refugees, Immigrants and Migrants.
More information: Nasreen S. Quadri et al, Evaluation of Preferred Language and Timing of COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake and Disease Outcomes, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.7877