This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Novel genetic scoring system helps determine ALS disease risk
Among the tens of thousands of Americans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, most do not have a single genetic mutation shown to cause the fatal disease.
And a study led by University of Michigan finds that a newly created polygenic scoring system—one that weighs the combined effects of common genetic variants—can improve the ability to predict an individual's risk of developing ALS. The results are published in Neurology Genetics.
"This polygenic scoring system we developed for ALS allows us to better understand the genetic architecture of the disease," said senior author Stephen Goutman, M.D., a neurologist and director of the Pranger ALS Clinic at U-M Health. "This may help to distinguish which populations have greater odds to develop the disease and inform future prevention studies and interventions."
Researchers took the genotypes of 219 patients with ALS and 223 healthy individuals without ALS, and they constructed the polygenic scores from a genome-wide association study of more than 80,000 people. An independent Spanish study sample was also used to replicate the analysis.
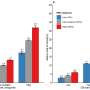
Investigators found that people with ALS had higher average polygenic scores than healthy control individuals and that an increase in polygenic score was associated with higher odds of having ALS.
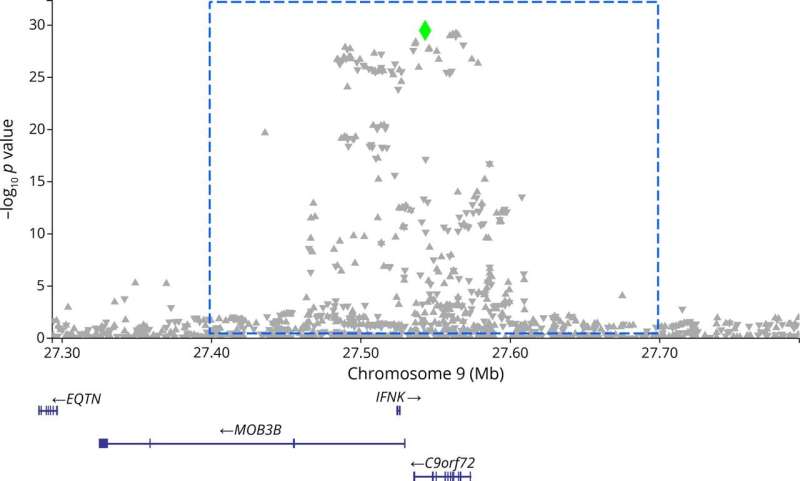
For the fraction of ALS cases caused by genetic factors, the researchers found that 4.1% were explained by a higher polygenic score. Additionally, mutations contributing to the polygenic score were present in genes involved in pathways and functions related to ALS disease progression and development.
"By combining all of the common genetic features previously associated with ALS, we improved ALS case status prediction among study populations in Michigan and in Spain," said co-author Kelly M. Bakulski, Ph.D., assistant professor of epidemiology at the U-M School of Public Health.
"However, there is a lot of room for improvement in ALS prediction so that folks at risk can be identified for prevention and treatment. Future research into additional risk factors, including environmental exposures, will be critical."
Since 1994, more than 40 genes have been associated with ALS, the most common being a mutation of the C9orf72 gene that is observed in over 40% of familial cases in a mixed European population.
Mounting research conducted at U-M has also found that environmental factors play a significant role in the onset and progression ALS.
Patients have reported higher occupational exposure to metals, combustion pollutants and volatile organic compounds prior to diagnosis. Those with elevated levels of pesticides and carcinogenic compounds in their blood were also found to have up to a fivefold higher risk of developing ALS.
"We call this combination of genetic and environmental factors the gene-time-environment hypothesis," said co-author Eva Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., director of the ALS Center of Excellence at U-M and James W. Albers Distinguished Professor of Neurology at U-M Medical School.
"Currently there is no biomarker or tool that can definitively predict who will develop ALS later in life, and only around 15-20% of ALS is inherited. But even if the polygenic score can only explain a small number of individuals at risk, it could be an important screening method for risk reduction."
Replication of the polygenic scores and larger samples, researchers say, are essential to determine if the results are generalizable across all populations.
"Including samples from a diverse range of populations will improve our ability to predict ALS in a majority of people," said co-author Bryan Traynor, M.D., Ph.D., a neurologist and senior investigator at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health.
More information: John Dou et al, Cumulative Genetic Score andC9orf72Repeat Status Independently Contribute to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Risk in 2 Case-Control Studies, Neurology Genetics (2023). DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200079