This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Video games spark exciting new frontier in neuroscience
University of Queensland researchers have used an algorithm from a video game to gain insights into the behavior of molecules within live brain cells.
Dr. Tristan Wallis and Professor Frederic Meunier from UQ's Queensland Brain Institute came up with the idea while in lockdown during the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Combat video games use a very fast algorithm to track the trajectory of bullets, to ensure the correct target is hit on the battlefield at the right time," Dr. Wallis said. "The technology has been optimized to be highly accurate, so the experience feels as realistic as possible.
"We thought a similar algorithm could be used to analyze tracked molecules moving within a brain cell."
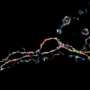
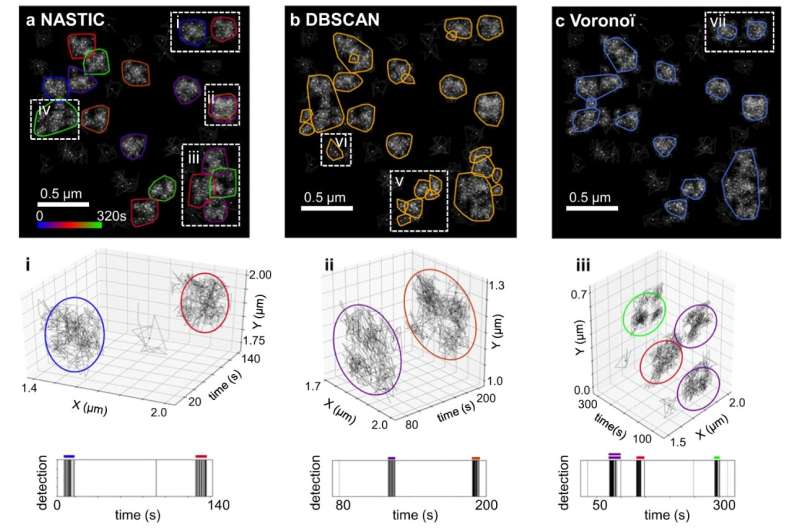
Until now, technology has only been able to detect and analyze molecules in space, and not how they behave in space and time.
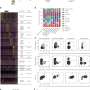
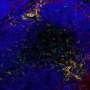
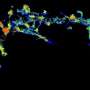
"Scientists use super-resolution microscopy to look into live brain cells and record how tiny molecules within them cluster to perform specific functions," Dr. Wallis said. "Individual proteins bounce and move in a seemingly chaotic environment, but when you observe these molecules in space and time, you start to see order within the chaos.
"It was an exciting idea—and it worked."
Dr. Wallis used coding tools to build an algorithm that is now used by several labs to gather rich data about brain cell activity.
"Rather than tracking bullets to the bad guys in video games, we applied the algorithm to observe molecules clustering together—which ones, when, where, for how long and how often," Dr. Wallis said. "This gives us new information about how molecules perform critical functions within brain cells and how these functions can be disrupted during aging and disease."
Professor Meunier said the potential impact of the approach was exponential.
"Our team is already using the technology to gather valuable evidence about proteins such as Syntaxin-1A, essential for communication within brain cells," Professor Meunier said. "Other researchers are also applying it to different research questions. And we are collaborating with UQ mathematicians and statisticians to expand how we use this technology to accelerate scientific discoveries."
Professor Meunier said it was gratifying to see the effect of a simple idea. "We used our creativity to solve a research challenge by merging two unrelated high-tech worlds, video games and super-resolution microscopy," he said. "It has brought us to a new frontier in neuroscience."
The paper is published in the journal Nature Communications.
More information: Tristan P. Wallis et al, Super-resolved trajectory-derived nanoclustering analysis using spatiotemporal indexing, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38866-y