This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
CT with CTA versus MRI in patients with dizziness
According to a study published in the American Journal of Roentgenology, patients discharged from the emergency department (ED) after CT with CTA alone could have benefitted from an alternative or additional MRI evaluation, including using a specialized abbreviated protocol for the modality.
Compared with those patients discharged after CT with CTA only, "the use of MRI in select patients presenting to the ED with dizziness was associated with greater frequency of critical neuroimaging results, greater use of echocardiography, and greater frequency of a change in secondary stroke prevention medications," concluded first author Long H. Tu, MD, from the department of radiology and biomedical imaging at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, CT.
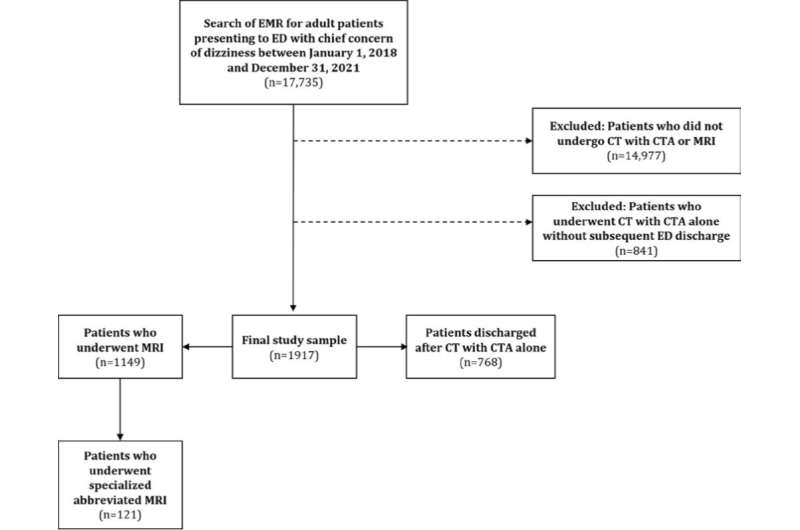
The study included 1,917 patients (776 men and 1,141 women; mean age, 59.5 years) presenting to the ED with dizziness from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2021. The initial propensity score matching analysis incorporated demographic characteristics, medical history, systems review, physical examination findings, as well as clinical symptoms to construct matched patients discharged from the ED after undergoing head CT with head and neck CTA alone and patients who underwent brain MRI—with or without CT and CTA.
Upon comparing those outcomes, a secondary assessment matched patients discharged after CT with CTA alone and patients who underwent specialized abbreviated MRI (i.e., multiplanar high-resolution DWI with ≤3 mm slice thickness) for increased sensitivity for posterior circulation stroke.
Ultimately, patients with dizziness undergoing MRI, versus CT with CTA alone, showed greater frequency of change in secondary stroke prevention medication (9.6% vs. 3.2%) and subsequent echocardiography (6.4% vs. 1.0%). Again, versus CT with CTA alone, Tu and colleagues' specialized abbreviated MRI protocol was also associated with lower frequency of 90-day ED readmissions (12.0% vs. 28.0%).
"When available," the authors acknowledged, "use of MRI may motivate clinically impactful management changes in patients presenting with dizziness."
More information: Long Hu et al, CT With CTA Versus MRI in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dizziness: Analysis Using Propensity Score Matching, American Journal of Roentgenology (2023). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.23.29617. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37404082/