This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Navigating telemedicine implementation: Exploring experiences of primary care clinicians early in the COVID-19 pandemic
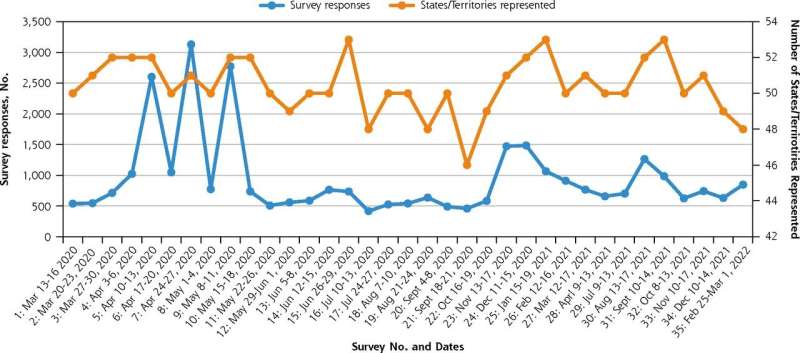
Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Case Western Reserve University conducted weekly and monthly surveys of primary care clinicians to examine the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. The e-surveys were conducted between March 2020 and March 2022 and used convenience sampling. A total of 36 surveys were completed, with an average of 937 respondents per survey, representing clinicians from all 50 states and from multiple specialties.
Initially, respondents reported difficulties in implementing telemedicine, citing challenges with infrastructure and reimbursement mechanisms. However, as time progressed, attitudes toward telemedicine became more positive, and clinicians recognized video- and phone-based care as valuable tools in their practice—though not a complete substitute for in-person care.
The COVID-19 pandemic compelled health care staff to rapidly adopt telemedicine tools to ensure continued care while prioritizing patient safety. Medical personnel encountered several challenges during the early stages of adopting telehealth models of care, including limited access to infrastructure for conducting consultations, issues with reimbursement rates for telemedicine services, the necessity to redesign workflows, and the need for comprehensive training.
Although there were initial implementation challenges during the pandemic, primary care professionals now recognize the advantages of integrating telemedicine into their practices and view technology as a valuable complement to their care delivery. However, researchers assert that their survey findings on the adoption and utilization of video- and phone-based care during the pandemic help identify potential obstacles, including implementation barriers and payment methods.
The research is published in The Annals of Family Medicine journal.
More information: Rebecca S. Etz et al, Telemedicine in Primary Care: Lessons Learned About Implementing Health Care Innovations During the COVID-19 Pandemic, The Annals of Family Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1370/afm.2979