This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Aging and ovariectomy induces parallel phosphoproteomic changes in skeletal muscle of female mice
A new research paper titled "Natural aging and ovariectomy induces parallel phosphoproteomic alterations in skeletal muscle of female mice" has been published in Aging.
The loss of skeletal muscle strength mid-life in females is associated with the decline of estrogen. In this new study, researchers Mina P. Peyton, Tzu-Yi Yang, LeeAnn Higgins, Todd W. Markowski, Kevin Murray, Cha Vue, Laurie L. Parker, and Dawn A. Lowe from the University of Minnesota questioned how estrogen deficiency might impact the overall skeletal muscle phosphoproteome after contraction, as force production induces phosphorylation of several muscle proteins.
The researchers note, "Importantly, identification of these altered phosphosites and candidate kinases and phosphatases sensitive to the presence of estrogen will help advance our understanding of the contributions of estrogen deficiency to muscle strength loss in aging females."
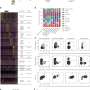
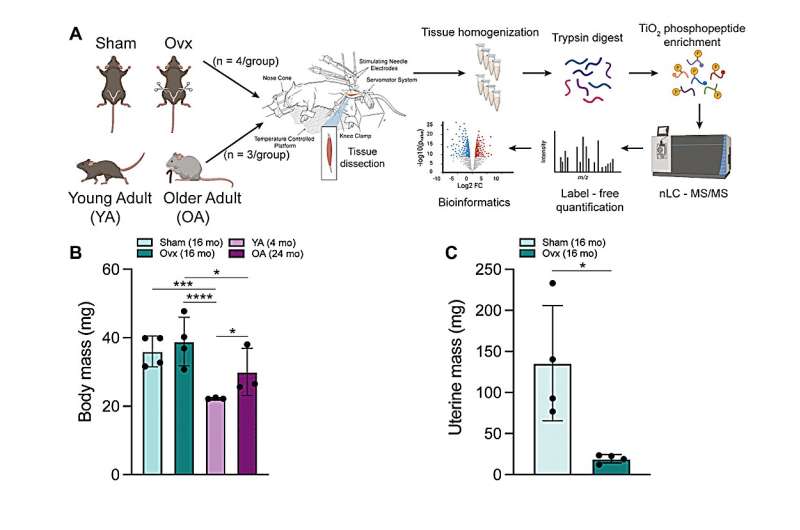
Phosphoproteomic analyses of the tibialis anterior muscle after contraction in two mouse models of estrogen deficiency, ovariectomy (ovariectomized [Ovx] vs. Sham) and natural aging-induced ovarian senescence (older adult [OA] vs. young adult [YA]), identified a total of 2,593 and 3,507 phosphopeptides in Ovx/Sham and OA/YA datasets, respectively. Further analysis of estrogen deficiency-associated proteins and phosphosites identified 66 proteins and 21 phosphosites from both datasets. Of these, 4 estrogen deficiency-associated proteins and 4 estrogen deficiency-associated phosphosites were significant and differentially phosphorylated or regulated, respectively.
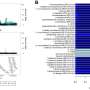
Comparative analyses between Ovx/Sham and OA/YA using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) found parallel patterns of inhibition and activation across IPA-defined canonical signaling pathways and physiological functional analysis, which were similarly observed in downstream GO, KEGG, and Reactome pathway overrepresentation analysis pertaining to muscle structural integrity and contraction, including AMPK and calcium signaling. IPA Upstream regulator analysis identified MAPK1 and PRKACA as candidate kinases and calcineurin as a candidate phosphatase sensitive to estrogen.
"In summary, our results from contracted skeletal muscle highlight CAST Ser-82 as a candidate phosphosite, and MAPK1/ERK2, PRKACA, and calcineurin as candidate upstream regulators sensitive to estrogen deficiency that may contribute to changes in the force-generating capacity of skeletal muscle," the team concludes.
More information: Mina P. Peyton et al, Natural aging and ovariectomy induces parallel phosphoproteomic alterations in skeletal muscle of female mice, Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204959