This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Dectin-1 stimulation promotes distinct inflammatory signature in HIV and aging: Study
A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging, titled "Dectin-1 stimulation promotes a distinct inflammatory signature in the setting of HIV-infection and aging."
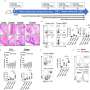
Dectin-1 is an innate immune receptor that recognizes and binds β-1, 3/1, 6 glucans on fungi. In this new study, researchers Archit Kumar, Jiawei Wang, Allen Esterly, Chris Radcliffe, Haowen Zhou, Brent Vander Wyk, Heather G. Allore, Sui Tsang, Lydia Barakat, Subhasis Mohanty, Hongyu Zhao, Albert C. Shaw, and Heidi J. Zapata from Yale University evaluated Dectin-1 function in myeloid cells in a cohort of HIV-positive and HIV-negative young and older adults.
"To our knowledge, our study is the first to evaluate the specific function of Dectin-1 in the setting of aging and HIV-infection," say the researchers.
"The HIV-positive and HIV-negative groups were comparable in age and gender distribution, incidence of comorbidities such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease and pulmonary disease."
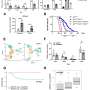
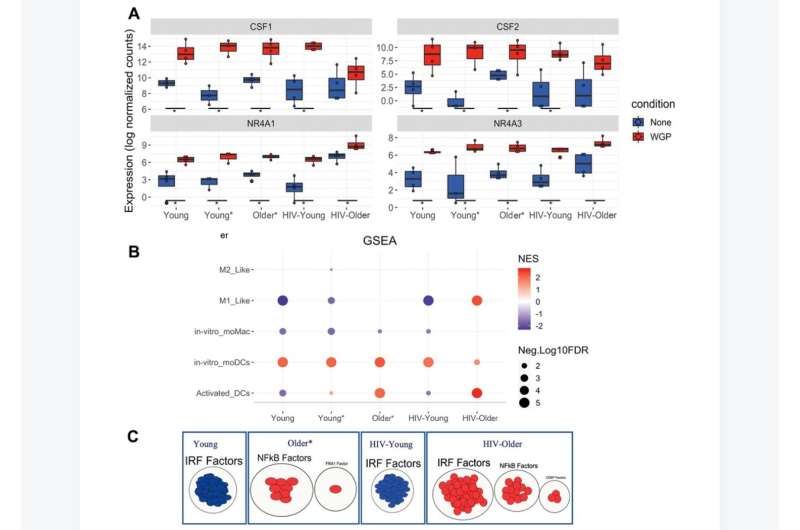
Stimulation of monocytes with β-D-glucans induced a pro-inflammatory phenotype in monocytes of HIV-infected individuals that was characterized by increased levels of IL-12, TNF-α, and IL-6, with some age-associated cytokine increases also noted. Dendritic cells showed a striking HIV-associated increase in IFN-α production. These increases in cytokine production paralleled increases in Dectin-1 surface expression in both monocytes and dendritic cells that were noted with both HIV and aging.
Differential gene expression analysis showed that HIV-positive older adults had a distinct gene signature compared to other cohorts characterized by a robust TNF-α and coagulation response (increased at baseline), a persistent IFN-α and IFN-γ response, and an activated dendritic cell signature/M1 macrophage signature upon Dectin-1 stimulation.
Dectin-1 stimulation induced a strong upregulation of MTORC1 signaling in all cohorts, although increased in the HIV-Older cohort (stimulation and baseline). In sum, this study demonstrates that the HIV Aging population has a distinct immune signature in response to Dectin-1 stimulation. This signature may contribute to the pro-inflammatory environment that is associated with HIV and aging.
"Overall, this study demonstrates that age, HIV-infection and co-morbidities can alter the individual immune response. In particular our study showed a unique immune signature in the setting of both HIV and aging in response to Dectin-1 stimulation," say the authors.
More information: Archit Kumar et al, Dectin-1 stimulation promotes a distinct inflammatory signature in the setting of HIV-infection and aging, Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204927