This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Potential Alzheimer's treatment would use high-frequency terahertz radiation
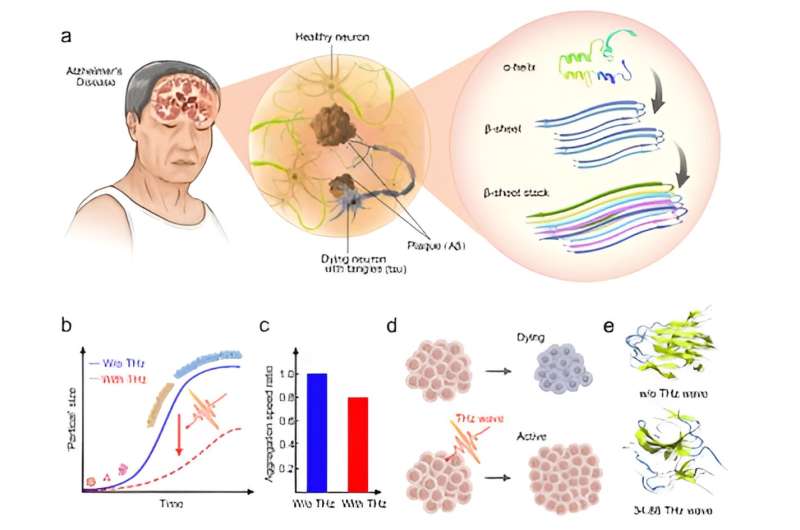
Amyloid deposition is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). The deposition process is described as a sigmoidal curve in which the misfolded proteins assemble into oligomers before fibril elongation. This dynamic process is accompanied by the misfolded monomer with more α-helix formed into abundant crosslinked β-sheet structure. Targeting the toxic accumulation may represent a promising strategy to slow or prevent disease initiation.
In a new paper published in eLight, a team of scientists, led by Professor Chao Chang from Peking University, has developed a unique technique that uses a specific frequency to regulate and minimize the development of amyloid deposition.
It was conjectured in 2018 that the physical field of biological neural signals might be a high-frequency electromagnetic field ranging from terahertz (THz) to infrared (IR). It is most likely to range from 0.5 to 100 THz and is named a generalized THz electromagnetic (EM) wave. Some physiological processes have been proven, such as the unwinding of DNA hairpins; the permeability of the voltage-gated calcium channel and the currents of voltage-gated K+ can regulate that. The mechanism revealed that the THz wave resonates with the molecular population and modifies the hydrogen bond (H-bond) formed therein. Moreover, it was reported that the intermolecular H-bond network that parallels the fibril axis is the key to leading the amyloid fibrils.
With this knowledge, it would be essential to prevent or mitigate AD pathology if resonant features could be exploited to modulate the self-assembly process and avoid undesired protein aggregation. An earlier study found that a 1,675cm-1 (50.25 THz) light could dissociate the amyloid fibrils by a joint free-electron laser experiment and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation method. There was a significant thermal effect at this frequency because the biological liquid has a strong absorption at the range of 45-52.5 THz. It results in the regulated efficiency in the physiological environment being bound to be considerably weakened. Therefore, exploring nonthermal and efficient methods to inhibit the Aβ aggregation process is urgent.
The research team used amyloid β (Aβ) as an example to conduct the research. It does not claim that Aβ plays the determining role in AD development, so more and more research has begun to emphasize the significance of tau protein. Amyloid proteins have similar dynamic aggregation processes. There are still no effective drugs that can inhibit or alleviate the deterioration of AD pathology.
The study intended to regulate the conformations of pathological proteins by optical means that intervene in the dynamic process. This research based on Aβ may be further applied to tau protein, which is of great significance for developing combination therapy.
The research team used the quantum cascade laser (QCL) with a central frequency of 34.88 THz (8.6 µm) to irradiate the Aβ1-42 oligomers. They monitored the fibrosis process by Thioflavine T (ThT) binding assay and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer. The research team found that the fibrosis process has been slowed down significantly compared to the group without an external field. The safety of this frequency on the cell level has also been detected through cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential assays.
It was noted that the cells proliferated significantly, and there was a slight increase in mitochondrial membrane potential. This demonstrates that the THz waves may positively affect the cells' function. The research team also found a significant change in protein conformation, which presents from the regularly ordered structure to a disordered structure, specifically, with more β-sheet structure transformed to the coil and bend region. THz waves may be a promising strategy to delay the amyloid fibrillation process.
More information: Wenyu Peng et al, High-frequency terahertz waves disrupt Alzheimer's β-amyloid fibril formation, eLight (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s43593-023-00048-0