This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Radiologists must monitor novel Alzheimer's treatment side effect, says study
A new article published in RadioGraphics examines the use of monoclonal antibody therapies for treating Alzheimer's disease and alerts physicians to be on the lookout for a potential side effect: amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA).
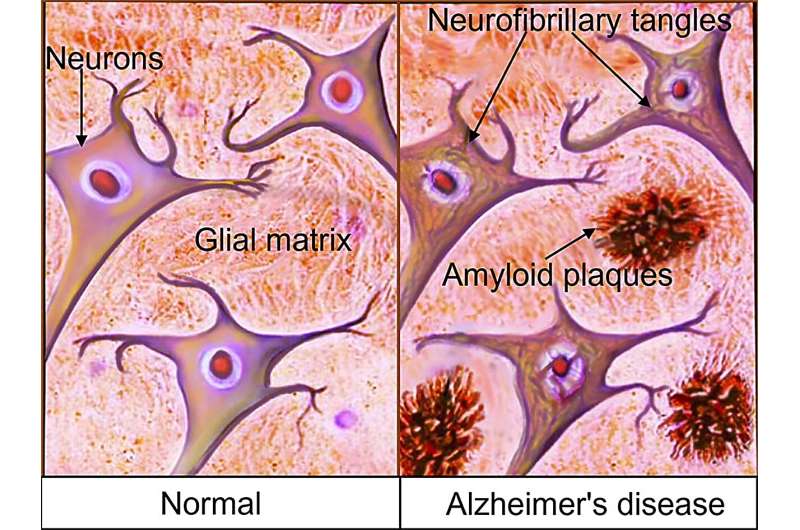
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive, irreversible brain disorder that slowly degrades memory and cognitive function. It is the most common form of dementia worldwide. While previous treatment methods focused on addressing Alzheimer's disease symptoms, recent approvals of monoclonal antibodies have provided a path to target the underlying disease itself.
The main pathologic feature of Alzheimer's disease is a buildup of toxic amyloid-B. Disease-modifying drugs like monoclonal antibodies work by clearing toxic amyloid-B protein from the brain. In June 2021, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave accelerated approval for aducanumab (Aduhelm) as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease. The FDA has determined that there is substantial evidence that aducanumab reduces amyloid-B plaques in the brain and that the reduction in these plaques is likely to result in benefits to patients.
"FDA-approved drugs such as aducanumab, as well as upcoming newer-generation drugs, have provided an exciting new therapy focused on reducing the amyloid plaque burden in Alzheimer disease," said Amit K. Agarwal, M.B.B.S., M.D., lead author of the article and neuroradiologist at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida.
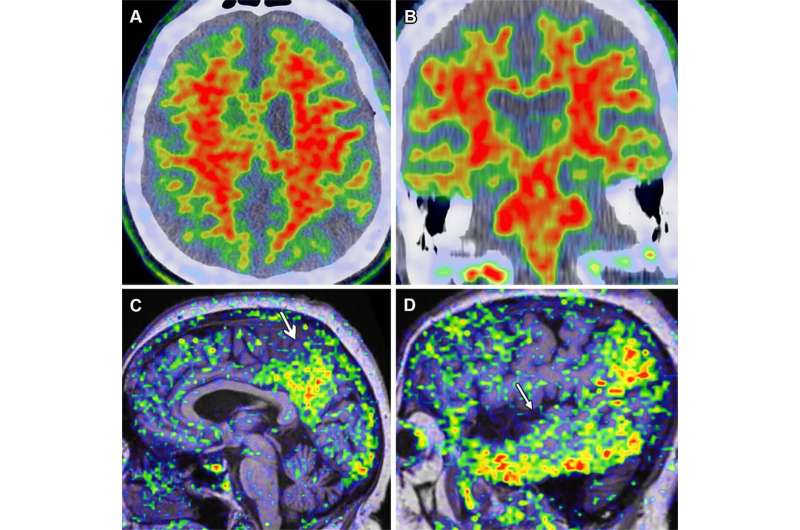
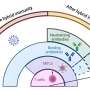
Although this groundbreaking new therapy has shown benefits in Alzheimer's patients, it is not without complications. Increased use of monoclonal antibodies led to the discovery of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA). The abnormalities have been further classified into two categories, ARIA-E, representing edema (swelling) and/or effusion, and ARIA-H, representing hemorrhage. ARIA is thought to be caused by increased vascular permeability following an inflammatory response, leading to the leakage of blood products and fluid into surrounding tissues.
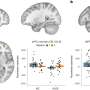
Patients with ARIA sometimes have headaches, but they are usually asymptomatic and only diagnosable with MRI.
"It is essential for the radiologist to recognize and monitor ARIA," Dr. Agarwal said. "As the use of monoclonal antibodies becomes more widespread, close collaboration between neurologists and radiologists is needed before and during therapy to plan for image monitoring per established guidelines."
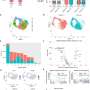
ARIA-E is the most common side effect of monoclonal antibody treatment. In two phase III trials, 35% of patients on the approved dose had ARIA-E. These trials also showed that most ARIA-E cases were clinically asymptomatic and that 98% were resolved at follow-up imaging. ARIA-E occurred most frequently between three and six months of treatment, with incidence sharply dropping after the first nine months. ARIA-H typically occurs in about 15 to 20% of patients treated with monoclonal antibodies. Unlike ARIA-E, ARIA-H is not transient and does not resolve over time.
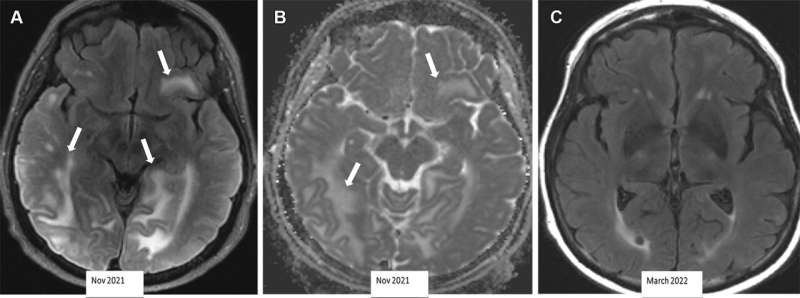
Most patients with asymptomatic ARIA meeting specific radiographic and clinical criteria may continue to receive treatment. The vast majority of patients with ARIA-E can continue therapy either with or without temporary suspension. However, in ARIA-H patients, therapy decisions depend on the severity of ARIA-H and whether it is stabilized. The detection of 10 or more new microhemorrhages requires permanent discontinuation of therapy.
"Immunotherapy is becoming more prevalent in managing dementia, and the recently approved monoclonal antibody therapy offers an exciting new frontier," Dr. Agarwal said. "Identifying and monitoring ARIA plays a vital role in safety monitoring and management decisions in anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody trials and clinical practice."
According to Dr. Agarwal, when ARIA is present, a conservative monitoring plan should be established with a multidisciplinary approach that includes neurologists and radiologists familiar with the clinical and imaging aspects of the condition.
More information: Amit Agarwal et al, Amyloid-related Imaging Abnormalities in Alzheimer Disease Treated with Anti–Amyloid-β Therapy, RadioGraphics (2023). DOI: 10.1148/rg.230009