This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Study finds connection between gut microbiome and bone density
There is growing evidence that a relative abundance of certain gut microbes may be related to skeletal health, according to a new study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology. If confirmed by additional research, the findings could provide the opportunity to alter gut microbiomes to achieve better bone health, as scientists learn more about "osteomicrobiology," a new term recently used to characterize this relationship.
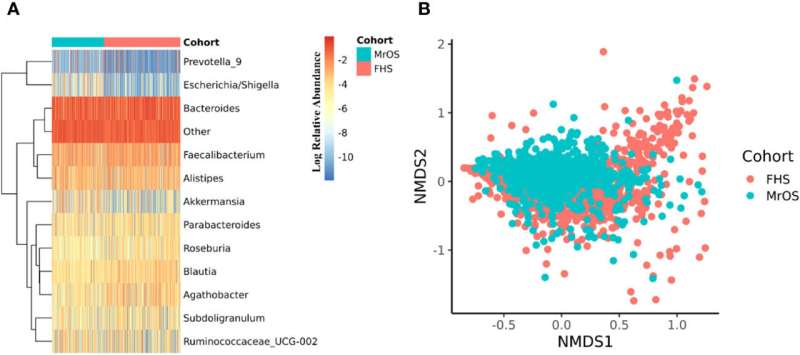
Due to the lack of large-scale human studies of the gut microbiome and skeletal health, researchers led by Paul C. Okoro, Data Scientist II at Hebrew SeniorLife and Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, and principal investigator Douglas P. Kiel, M.D., M.P.H., Senior Scientist at the Marcus Institute, conducted an observational study based on the Framingham Third Generation Study of men and women, and the Osteoporotic fractures in Men (MrOS) study of older men to determine whether they could find a potentially modifiable factor contributing to skeletal health.
The study used high-resolution imaging of the arm and leg.
This is significant because low bone density increases the risk of developing osteoporosis, affecting more than 10 million Americans over the age of 50, and can increase the risk of fractures.
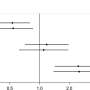
Titled "A Two-Cohort Study on the Association between the Gut Microbiota and Bone Density, Microarchitecture, and Strength," the study found that bacteria called Akkermansia, which has been associated with obesity, and Clostridiales bacterium DTU089, had negative associations with bone health for older adults.
DTU089, a bacterium from the class, Clostridia, has been described to be more abundant in people with lower physical activity, and lower protein intake, and could be significant because prior studies have found protein intake and physical activity have a definite connection to skeletal health.
"We found patterns in which greater abundance of microbiota were associated with worse measures of bone density and microarchitecture. In fact, some bacteria were associated with differences in the bone cross sectional area, suggesting the possibility that certain microbes could influence how the bone changes size with aging," said Dr. Kiel.
"It is premature to know if the bacterial organisms themselves may have effects on skeletal health. With additional studies we might be able to gain insights regarding associations between specific bacterial species in the intestine and skeletal integrity. We also hope to identify specific functional pathways influenced by the bacteria that could influence the skeleton."
"For example, some bacteria can lead to low levels of inflammation that may affect bone health. Ultimately, if findings like this are confirmed, we may be able to target the gut microbiome to influence skeletal health."
More information: Paul C. Okoro et al, A Two-Cohort Study on the Association between the Gut Microbiota and Bone Density, Microarchitecture, and Strength, Frontiers in Endocrinology (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1237727 www.frontiersin.org/articles/1 … /fendo.2023.1237727/