This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Key regulators involved in genesis of multiple sclerosis lesions identified
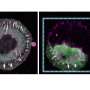
By means of CRISPR screening, LMU researchers have provided the first ever comprehensive molecular characterization of T cell infiltration into the central nervous system of people with MS.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common disabling disease of the central nervous system (CNS) in young adults. The disease is initiated when activated autoreactive T cells infiltrate the CNS and trigger a cascade of tissue injury. The importance of this T cell infiltration is well evidenced from studies in rodent models of the disease and in humans.
"Despite this knowledge, we lacked a comprehensive understanding of the essential molecules that regulate the migration of autoreactive T cells to the the CNS," says Martin Kerschensteiner, Director of the Institute of Clinical Neuroimmunology at LMU. This was a knowledge deficit that a team led by Kerschensteiner and Naoto Kawakami at LMU's Biomedical Center Munich sought to remedy.
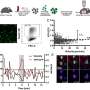
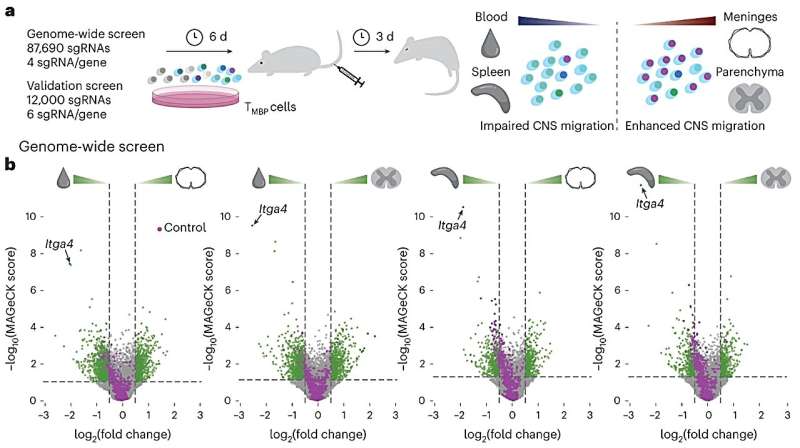
As the researchers report in Nature Neuroscience, they were able to identify five essential inhibitors and 18 essential facilitators of T cell migration to the CNS using a genome-wide analysis.
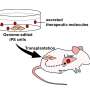
Genome-wide in vivo CRISPR screen in rat model
The Munich researchers employed a gene editing approach that had not previously been used in connection with MS models. "CRISPR technology raises the possibility of conducting comprehensive and unbiased loss-of-function screens in disease models in vivo," explains Kawakami. Before now, genome-wide CRISPR screens have largely been utilized in investigations relating to cancer pathogenesis, but not yet in relation to MS.
"We used a rodent MS model and combined an unbiased genome-wide CRISPR screen with functional in vivo validation studies, multiphoton microscopy, and in vitro mechanistic experiments, to provide a definite molecular characterization of the central step in MS pathogenesis, the infiltration of autoreactive T cells to the CNS," says Kawakami.
In total, the researchers identified five essential inhibitors and 18 essential facilitators of this mechanism.
Basically, these regulators can be ascribed to three functional categories, which are necessary for a T cell to cross over from the blood to the brain. The adhesion of T cells to the endothelium of blood vessels through the molecule alpha-4 integrin is an important process at the beginning of transmigration.
In the next step, the T cells egress from the blood vessel. Their movement is controlled by messengers, which are recognized by a specific protein, the chemokine receptor CXCR3. The third functional category relates to molecules that regulate how T cells register attractive signals from the blood.
According to Kerschensteiner, the chief benefits of the study are twofold. "Our investigation has confirmed for the autoreactive T cells we studied that key molecules of the mechanism are already the target of MS therapies and are being employed in clinical practice."
Moreover, he adds, the approach taken by the researchers, which has now been validated also with regard to transferability to humans, can be applied to further less well understood questions, such as the migration of other harmful immune cell populations from the blood to the nervous system.
More information: Arek Kendirli et al, A genome-wide in vivo CRISPR screen identifies essential regulators of T cell migration to the CNS in a multiple sclerosis model, Nature Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01432-2