This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Visualizing nerves with photoacoustic imaging
Invasive medical procedures, such as surgery requiring local anesthesia, often involve the risk of nerve injury. During operation, surgeons may accidentally cut, stretch, or compress nerves, especially when mistaking them for some other tissue. This can lead to long-lasting symptoms in the patient, including sensory and motor problems. Similarly, patients receiving nerve blockades or other types of anesthesia can suffer from nerve damage if the needle is not placed at the correct distance from the targeted peripheral nerve.
Consequently, researchers have been trying to develop medical imaging techniques to mitigate the risk of nerve damage. For instance, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help a surgeon pinpoint the location of the nerves during a procedure. However, it is challenging to tell the nerves apart from surrounding tissue in ultrasound images, while MRI is expensive and time-consuming.
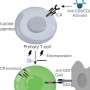
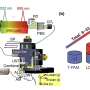
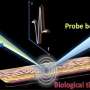
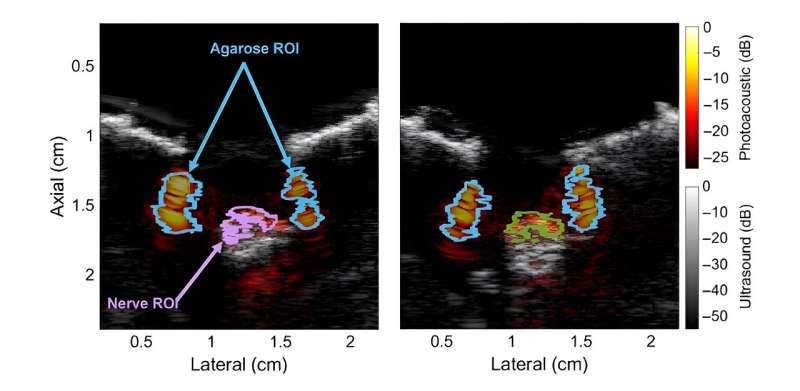
In this regard, there is a promising alternative approach known as multispectral photoacoustic imaging. A noninvasive technique, photoacoustic imaging combines light and sound waves to create detailed images of tissues and structures in the body. Essentially, the target region is first illuminated with pulsed light, causing it to heat up slightly. This, in turn, causes the tissues to expand, sending out ultrasonic waves that can be picked up by an ultrasound detector.
A research team from Johns Hopkins University recently conducted a study in which they thoroughly characterized the absorption and photoacoustic profiles of nerve tissue across the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum. Their work, published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, was led by Dr. Muyinatu A. Lediju Bell, John C. Malone Associate Professor and PULSE Lab Director at Johns Hopkins University.
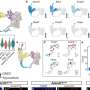
One of the main objectives of their study was to determine the ideal wavelengths for identifying nerve tissue in photoacoustic images. The researchers hypothesized that the wavelengths from 1630–1850 nm, which reside within the NIR-III optical window, would be the optimal range for nerve visualization, since the lipids found in the myelin sheath of neurons have a characteristic absorption peak in this range.
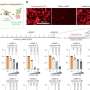
To test this hypothesis, they performed detailed optical absorption measurements on peripheral nerve samples obtained from swine. They observed an absorbance peak at 1210 nm, which fell in the NIR-II range. However, such an absorption peak is also present in other types of lipids. In contrast, when the contribution of water was subtracted from the absorbance spectrum, nerve tissue exhibited a unique peak at 1725 nm in the NIR-III range.
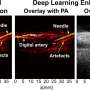
Additionally, the researchers conducted photoacoustic measurements on the peripheral nerves of live swine using a custom imaging setup. These experiments further confirmed the hypothesis that the peak in the NIR-III band can be effectively leveraged to differentiate lipid-rich nerve tissue from other types of tissues and materials containing water or that are lipid-deficient.
Satisfied with the results, Bell remarks, "Our work is the first to characterize the optical absorbance spectra of fresh swine nerve samples using a wide spectrum of wavelengths, as well as the first to demonstrate in-vivo visualization of healthy and regenerated swine nerves with multispectral photoacoustic imaging in the NIR-III window."
Overall, these findings could motivate scientists to further explore the potential of photoacoustic imaging. Moreover, the characterization of the optical absorbance profile of nerve tissue could help improve nerve detection and segmentation techniques when using other optical imaging modalities.
"Our results highlight the clinical promise of multispectral photoacoustic imaging as an intraoperative technique for determining the presence of myelinated nerves or preventing nerve injury during medical interventions, with possible implications for other optics-based technologies. Our contributions thus successfully establish a new scientific foundation for the biomedical optics community," concludes Bell.
More information: Michelle T. Graham et al, Optical absorption spectra and corresponding in vivo photoacoustic visualization of exposed peripheral nerves, Journal of Biomedical Optics (2023). DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.28.9.097001