October 6, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Adding tirzepatide to basal insulin cuts HbA1c levels in people with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes
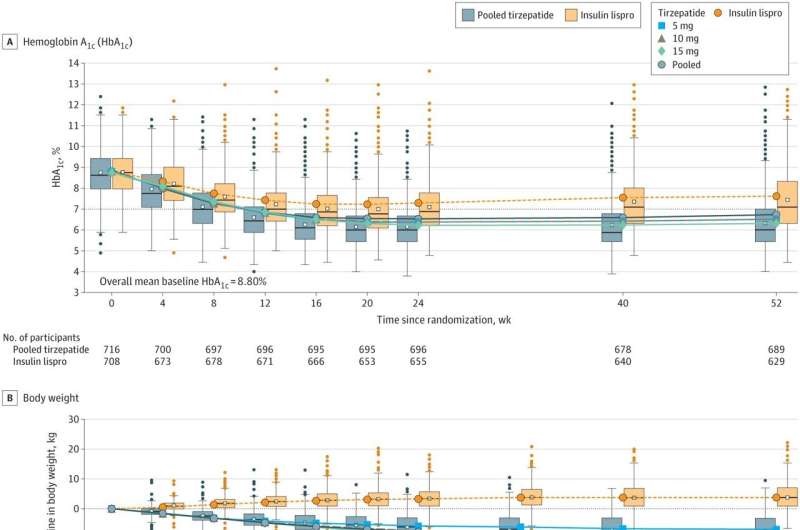
A team of medical researchers affiliated with multiple institutions in the U.S. working with a colleague from Spain has found via clinical trial that adding tirzepatide (brand name Mounjaro) to basal insulin therapies can reduce HbA1c levels in people with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. In their paper published in the journal JAMA, the group describes the parameters of the clinical trial and what they learned from it.
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), as its name suggests, is a type of hemoglobin that is found in red blood cells made by the body to transport oxygen. People with diabetes type 2 typically have more of it than normal, which is why it has become one of the standard blood tests given to patients with the disorder.
Prior research has shown that HbA1c can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and to make assessments of glycemic control. Prior research has also suggested that if a means could be found to reduce HbA1c levels, patients would see reductions in symptoms of the disorder. In this new effort, the research team conducted a phase IIIa clinical trial of a drug called tirzepatide , where it was used in conjunction with insulin.
The trial was carried out at 135 sites in 15 countries and ran from October 2020 to November 2022. In all, 1,428 adult type 2 diabetes patients participated in the trial—all the volunteers were also already using basal insulin injections to control their disease. In the trial, the researchers asked the volunteers to take tirzepatide once a week. The amount given varied by patient, from 5 mg to 15 mg. All the volunteers gave blood samples for testing every day of the trial, and 93% of them completed the trial.
The research team found that adding weekly doses of tirzepatide resulted in a mean reduction of -2.1% of HbA1c levels across all participants. They also found that more of the patients met A1c target goals. Prior research has shown that meeting such goals can help reduce damage caused to the body in diabetes patients, such as vision deterioration. The researchers also found that the volunteers were more successful in losing weight.
More information: Julio Rosenstock et al, Tirzepatide vs. Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes, JAMA (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.20294
© 2023 Science X Network