This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Combination therapy effective in the treatment of relapsed immune thrombocytopenia in adults
In the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), glucocorticoids and IVIg are considered the primary therapeutic options. Typically, clinicians opt for either of these treatments when addressing ITP cases. The research pertaining to the combined use of these two medications has predominantly focused on emergency situations and cases related to ITP during pregnancy. There has been limited investigation into the treatment of relapsed ITP in adult patients.
A new study by the Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, used a multicenter comprehensive retrospective analysis to assess the effectiveness and safety of primary single-agent and combination therapies in treating adult patients with relapsed immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). It represents the first attempt to compare the effectiveness of three treatment modalities (IVIg, glucocorticoids, or a combination of both) in enhancing platelet counts among adult relapsed ITP patients.
The findings from this research serve as a valuable reference for clinicians engaged in the management of ITP. The work is published in the journal Global Medical Genetics.
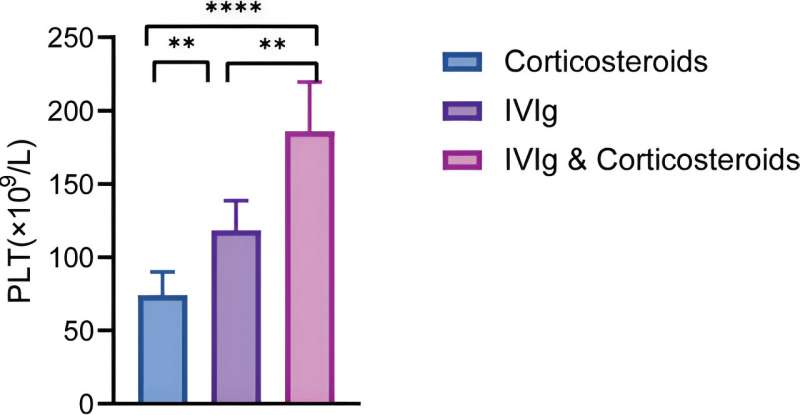
Professor Zhang Lei said, "Our study unveiled a remarkable finding: the combination therapy of IVIg and glucocorticoids in treating adult relapsed ITP patients led to a complete response (CR) rate of 71.83% within seven days, outperforming the IVIg group (43.48%) and the glucocorticoid group (23.08%). Moreover, the rate of improvement in platelet count and the daily proportions reaching 30×109/L, 50×109/L, and 100×109/L in the combination therapy group significantly differed from those in each single-agent group.
"Therefore, for relapsed persistent and chronic ITP patients, especially those requiring a rapid increase in platelet levels, relying solely on glucocorticoid medication might not be the most effective strategy. Combining IVIg to achieve superior efficacy is advisable.
"While patients responded similarly to IVIg and glucocorticoid drugs, it's noteworthy that the IVIg group exhibited a faster onset of action and superior treatment efficacy compared to the glucocorticoid group. Hence, when considering first-line single-agent therapy for adult relapsed ITP patients, prioritizing IVIg treatment is recommended.
"With the continuous advancement of biopharmaceutical technology, a plethora of new drugs and targeted therapies has expanded the clinical avenues for ITP patients. However, no clear consensus has been reached regarding the optimal medication sequence, leading more patients to prefer newer drugs and targeted therapies like TPO-RA, rituximab, Syk inhibitors, and Fcγ receptor inhibitors upon relapse. This diversity has introduced significant variations in ITP relapse treatments.
"Our findings indicate that for relapsed persistent and chronic ITP patients, the combination therapy approach involving first-line drugs offers advantages in both onset time and treatment efficacy. This rapid, stable, and high CR rate clinical efficacy is particularly beneficial for patients with low platelet counts and accompanying bleeding symptoms. Combination therapy can safely and effectively elevate platelet counts swiftly, achieving hemostasis and reducing the necessity for platelet transfusions."
Given that this study is retrospective, its level of evidence falls below that of prospective research. Consequently, it remains essential for clinical practitioners to make treatment choices in line with their clinical expertise and the unique circumstances of their patients. Furthermore, there is an aspiration that clinical research centers throughout the country will engage in more prospective studies for patients in similar situations in the future.
More information: Lijun Fang et al, Efficacy and Safety Analysis of Combination Therapy Consisting of Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Corticosteroids versus Respective Monotherapies in the Treatment of Relapsed ITP in Adults, Global Medical Genetics (2023). DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1769087