This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
How do we decide what to look at next? A computational model has the answer
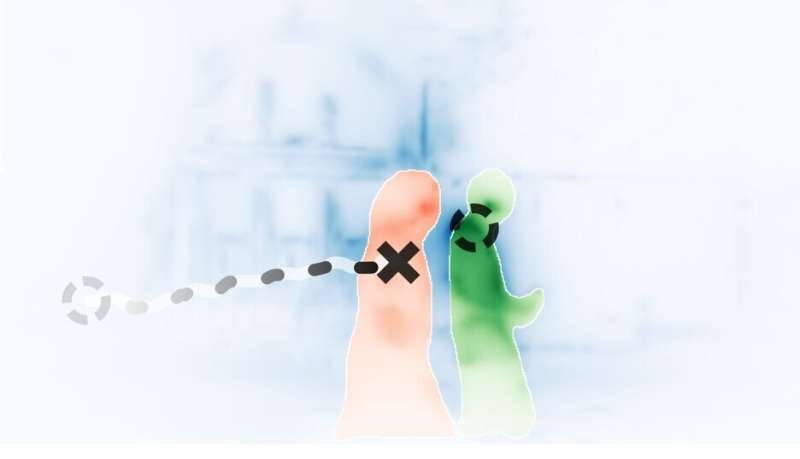

Imagine you are looking out the window: a small bird is flying across the blue sky, and a girl with a red baseball cap is walking along the sidewalk, passing by two people sitting on a bench. You might think that you are "just seeing" what is happening, but the truth is that to make sense of the world around us, we constantly make active decisions about where to look.
We typically move our eyes two to three times a second. But how do we decide when to move our eyes and where to look next? Is it the flapping of the bird's wings or the color of the baseball cap that is attracting our attention?
While psychologists and neuroscientists have been interested in these questions for a long time, a new study published in PLOS Computational Biology by Nicolas Roth, Martin Rolfs, Olaf Hellwich, and Klaus Obermayer from the Cluster of Excellence Science of Intelligence shed new light into the topic by simulating eye movement behavior using a computational modeling approach.
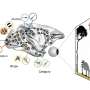
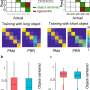
By comparing human eye tracking data with their simulations, the authors showed how important visual objects are for guiding our eye movements.
Based on the existing body of experimental evidence, the authors built a computational framework that models previously uncovered attentional mechanisms.
"The world around us is dynamic and much more complex than your typical stimulus in psychological experiments. These experiments are usually restricted to static images or compositions of simple geometrical forms, and previous models describing how humans explore their environments typically only work in such reduced scenarios. With our modeling framework, we found a simple but powerful approach to test different assumptions about how the visual system might work," said Nicolas Roth, the paper's main author.
Historically, computational models that predict what humans pay attention to are based on so-called "space-based attention." The idea is that the brain processes the whole visual field where everything we see is directly mapped onto a mental image of the scene from which it selects the next eye movement target. In such a map, conspicuous parts of the scene (like the location of the red color of the cap or the movement of the bird's wings) stand out and are consequently most likely to be selected as targets for the following eye movements.
There is, however, mounting evidence in favor of a competing view, where it is not the conspicuity of each location in this space that determines where to look next, but rather semantically defined objects.
In models assuming "object-based attention," the movement of wings would still be conspicuous, but it would immediately be processed as part of the flying bird. Similarly, such a model would not select the location of the most outstanding color in the scene as the next gaze position. Instead, it would first divide the scene into different objects and then, based on this representation, choose which object to look at based on its features like the color of a person's clothes.
"The difference between these two possible ways of how the brain represents potential eye movement targets might sound technical," said Roth. "Yet, investigating whether visual attention is space- or object-based is crucial for understanding how the brain organizes and acts on visual information. Therefore, we think that our finding of object-based models resulting in significantly more human-like eye movements is an important step in understanding the basic principles of how we achieve an understanding of the visual world."
This study can have important implications for the creation of artificial systems, such as robots.
"Since we can now model eye movements in dynamic real-world scenes, we can also transfer our insights to artificial systems that interact with the real world. For example, at the 'Science of Intelligence' cluster, we and our robotics colleagues are currently investigating how a robot benefits from actively moving its cameras to explore its environment using human-inspired object-based attention," said Roth.
More information: Nicolas Roth et al, Objects guide human gaze behavior in dynamic real-world scenes, PLOS Computational Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011512