This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Novel mechanism uncovered: PRMT1 advances gastric cancer progression via β-catenin signaling
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from Southwest University, and Southwest Medical University investigated PRMT1, a protein previously known to be overexpressed in gastric cancer cells. Using short hairpin RNA (shRNA) technology, they reduced the expression of PRMT1 in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells.
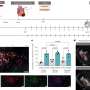
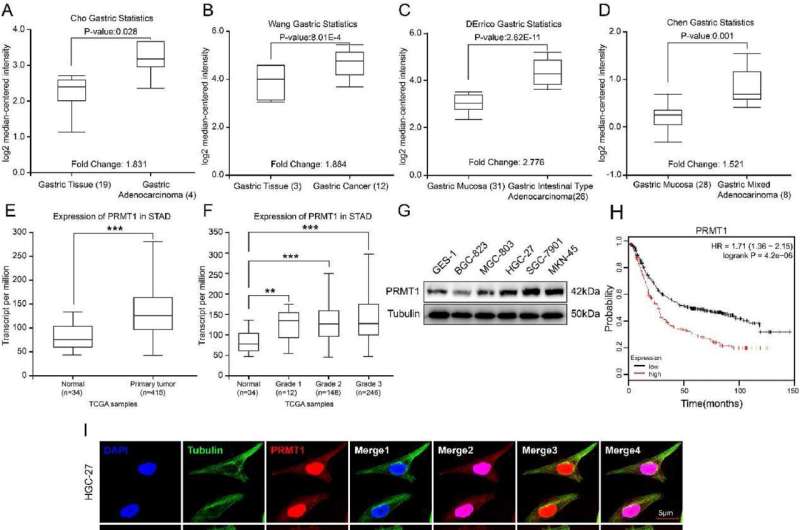
Additionally, they treated the cells with PRMT1 inhibitors to study the effects on cell proliferation and migration. The findings have unveiled a mechanism through which Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) promotes the proliferation and spread of gastric cancer (GC) cells. Analysis from the Oncomine and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases revealed a pronounced overexpression of PRMT1 in gastric cancer tissues, which is associated with poor patient prognosis.
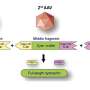
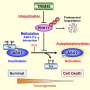
This overexpression plays a significant role in gastric cancer progression, as silencing PRMT1 diminishes the proliferation and migration rate of GC cells. Intriguingly, PRMT1 directly binds to and activates the β-catenin signaling pathway, a key player in cell growth and metastasis, by targeting its promoter.
The study also identified MLXIP, a transcription factor, as a PRMT1-binding protein, suggesting that PRMT1 possibly recruits MLXIP to the β-catenin promoter, further underlining its intricate role in GC dynamics. Additionally, Kinectin (KTN1) has been found to interact with PRMT1, offering another layer of regulation that could impact PRMT1's function in gastric cancer. The findings point toward new potential therapeutic targets for gastric cancer.
The study unveils a novel molecular mechanism of PRMT1's role in advancing gastric cancer, mediated by the β-catenin signaling pathway. The identified PRMT1-MLXIP-β-catenin axis could become a pivotal target for future therapeutic strategies against gastric cancer. These findings could pave the way for developing gene therapies targeting PRMT1 or associated pathways, offering hope to millions diagnosed with this aggressive cancer.
More information: Feng Wang et al, PRMT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by recruiting MLXIP for the transcriptional activation of the β-catenin pathway, Genes & Diseases (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.02.006