This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Brain imaging identifies biomarkers of mental illness

Research and treatment of psychiatric disorders are stymied by a lack of biomarkers—objective biological or physiological markers that can help diagnose, track, predict, and treat diseases. In a new study, researchers use a very large dataset to identify predictive brain imaging-based biomarkers of mental illness in adolescents. The work appears in Biological Psychiatry.
Traditionally, psychiatric disorders such as depression have been diagnosed based on symptoms according to subjective assessments. The identification of biomarkers to aid in diagnosis and treatment selection would greatly advance treatments.
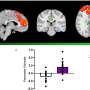
In the current study, the investigators used brain imaging data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study of nearly 12,000 children aged 9 to 10 at the beginning of the study. Modern neuroimaging techniques, including resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) analysis, allow researchers to investigate the organization of brain circuits through their interaction with one another over time.
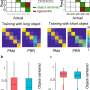
Yihong Yang, Ph.D., senior author of the study, at the Neuroimaging Research Branch, National Institute on Drug Abuse, said, "Using a functional MRI dataset, we identified a brain connectivity variate that is positively correlated with cognitive functions and negatively correlated with psychopathological measures."
Cognition has long been studied in the context of mental disorders, and recent research has pointed to shared neurobiology between the two, as supported in this new study.
This brain-based variate predicted how many psychiatric disorders were identified in participants at the time of the scan and over the following two years. It also predicted the transition of diagnosis across disorders over the two-year follow-up period."
Dr. Yang added, "These findings provide evidence for a transdiagnostic brain-based measure that underlies individual differences in developing psychiatric disorders in early adolescence."
John Krystal, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the work, "Mental illness in adolescence has emerged as a cardinal public health challenge in the post-COVID era. More than ever before, we would benefit from better ways to identify adolescents at risk. This study uses data from the landmark ABCD Study to illustrate how neuroimaging data could illuminate risk for mental illness across the spectrum of diagnoses."
Dr. Yang added, "Finding biomarkers of mental illnesses, rather than relying on symptoms, may provide a more precise means of diagnosis, and thereby aligning psychiatric diagnosis with other medical diagnoses."
More information: Xiang Xiao et al, Brain Functional Connectome Defines a Transdiagnostic Dimension Shared by Cognitive Function and Psychopathology in Preadolescents, Biological Psychiatry (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.08.028