This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Intensive rehabilitation can provide improvements long after stroke event
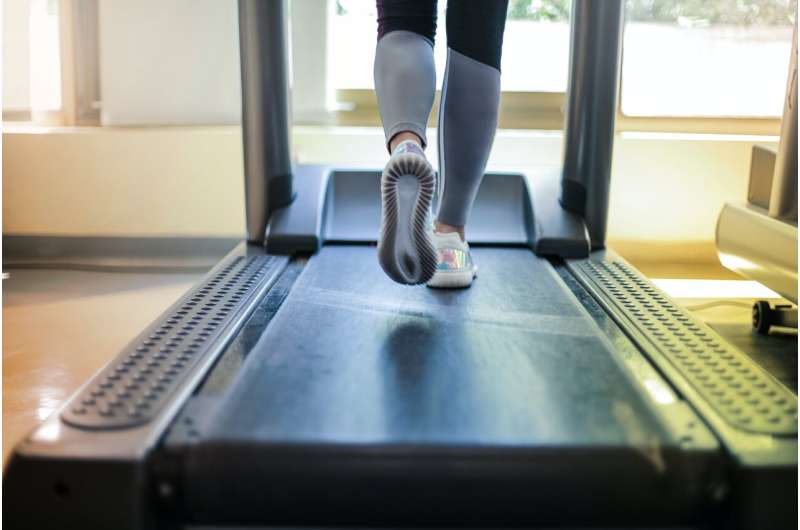

Lower-extremity constraint-induced movement therapy (LE-CIMT), i.e., high-intensity treatment with exercise six hours a day for two weeks, appears to improve the function of the leg and the ability to walk and move in its environment. The improvements are seen even if a long time has passed since the stroke, and the achieved effects were maintained, as shown in a new thesis by Ingela Marklund.
LE-CIMT is a treatment option that can be performed both in day rehabilitation in hospital and in outpatient care. People with stroke treated with LE-CIMT were interviewed for the study. Based on the patient's ability to walk a distance of six minutes, their health-related quality of life in terms of physical function can be predicted, emphasizing the importance of walking and locomotion training in post-stroke rehabilitation.
"We found that the high-intensity treatment produced significant improvements in leg function with increased strength, improved balance and the ability to walk and do two things at the same time," says Marklund, Department of Community Medicine and Rehabilitation.
Remaining improvements
In addition, walking speed and the ability to walk a longer distance improved in people with stroke. They maintained or even improved their weight bearing on the more affected leg to a more symmetrical load in standing. The improvements achieved were maintained at follow-up three and six months after the end of treatment.
"We also found a strong correlation between time since illness and age in the functional tests that were carried out. Those who completed LE-CIMT within six months of their illness improved their walking speed to a greater degree than those who completed LE-CIMT after seven months or more. Younger participants had better balance than older ones in one of the balance tests."
Analysis of the interviews conducted about the participants' experiences generated an overarching theme, that the LE-CIMT gave them knowledge about themselves and how their body works. This knowledge facilitated the possibility of living life more easily. They felt that there was still hope and opportunity for functional improvement, which gave them increased independence and self-esteem. Although the treatment was intense and challenging, it was felt to be absolutely necessary.
Increased participation
Compared to the general population in Sweden, the participants had a significantly lower health-related quality of life in terms of physical function, physical capacity, general health and social function. There was a strong correlation between their results on the six-minute walk test and the physical function domain.
"With increased function in the affected leg, conditions are created for increased participation in society for those who suffer a stroke. Strength, balance and the ability to walk and do two things at the same time are important factors in reducing the risk of falling," says Marklund.
More information: Lower-extremity constraint-induced movement therapy in individuals with stroke—Improvements, experiences and health-related quality of life. umu.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1807834&dswid=3870