This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Researchers cultivate lung tumors to identify optimal personalized treatments
Lung cancer accounts for nearly 20% of annual cancer-related deaths worldwide. According to 2022 statistics from the Swiss Cancer League, nearly 5,000 new cases of lung cancer are reported in Switzerland each year. Over the five years following diagnosis, only 1 in 5 people survives.
Chemotherapy and targeted therapy are the primary treatments offered to patients, but due to the heterogeneity of lung cancers, not all tumors respond to one or other of these treatments. Furthermore, cancer cells may develop resistance to treatment prompting consideration of combinations of several molecules.
To identify the most effective compound or combinations for each tumor, testing on ex vivo cultures of patients' tumors in the laboratory could be a solution. This methodology is the subject of a new study published in the journal Cancers.
A technology precisely described
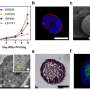
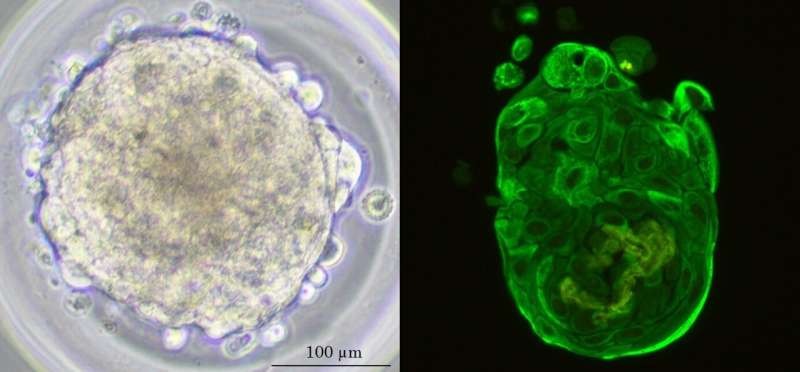
To closely recapitulate tumors in the laboratory, the 3D culture of cancer cells in the form of aggregates called spheroids has gained interest in the last decade. However, 3D culturing of lung cancer cells had been challenging and poorly documented until now. The team of researchers from the HUG and the UNIGE established and tested a spheroid model using tumor fragments obtained during surgical interventions.
Twenty-one patients with non-small-cell lung cancers were included in this study. They were managed by Dr. Wolfram Karenovics, Staff Physician in the Thoracic and Endocrine Surgery Division and Professor Alfredo Addeo, Head of the Oncology Division and responsible for the Lung Cancer Center at the HUG and Professor in the Department of Medicine at the Faculty of Medicine of the UNIGE, both co-authors of this study.
"Through a meticulous process of expansion and selection, we cultivated these cells into tumor spheroids in our laboratory incubators. In just 15 to 20 days, these spheroids—now robust and fully characterized—were exposed to anticancer treatments recommended by the oncologist to determine their effectiveness," explains Véronique Serre-Beinier, the study's lead author and head of the basic research laboratory of the Thoracic and Endocrine Surgery Division at the HUG and researcher in the Department of Surgery in the Faculty of Medicine of the UNIGE.
Toward personalized lung cancer treatment
There are two major types of lung cancers. The first one, the "non-small-cell" lung cancer, constitutes 4 out of 5 cases. This group includes three main subsets classified according to their morphology and mutations. Within approximately 15 days, all mutations expressed by tumor cells are identified to assess appropriate treatments.
"During these two weeks and thanks to our new methodology, we can now develop patient-derived tumor spheroids and then be ready to test the treatments selected by the oncologist—this is a significant advantage," explains the researcher. This methodology does not apply to the second type of lung cancers, the "small cell" lung cancer, accounting for 1 out of 5 cases, typically detected late when metastatic symptoms appear with unfortunately limited treatment options.
Applications against resistance and side effects
The literature indicates that 30% to 40% of individuals under targeted therapy will develop a resistance to the treatment. The spheroid cultures described in this study will help identify the most effective treatment for each patient and assess the risk of cancer cells adapting and developing resistance to treatments.
Anticancer treatments, especially chemotherapy, often induce undesirable side effects, by affecting healthy cells. The results of the study are encouraging in this regard as well. "We also obtained spheroids from healthy lung tissue from the same patients. These 'normal' spheroids help measure the toxicity of the drugs on healthy lung cells, thus avoiding harmful side effects," says Serre-Beinier.
Lung spheroid models offer hope in the quest for personalized cancer treatments and serve as a gateway for developing anticancer treatments tailored to each individual. "To reach this point, we still need to expand the application of tumor spheroids to complement the techniques developed so far in precision oncology," concludes Serre-Beinier.
More information: Amanda Mueggler et al, An Optimized Method to Culture Human Primary Lung Tumor Cell Spheroids, Cancers (2023). DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235576