This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
How childhood stress influences gene activity and increases the risk of mental illness
Many psychiatric illnesses are related to stress. Negative experiences in childhood can often affect how we deal with stress later in life. But what biological processes are involved? A study recently published in the journal Biological Psychiatry, conducted by researchers at the Central Institute of Mental Health (CIMH) in Mannheim, sheds more light on this.
"A deeper understanding of these biological processes holds considerable potential for improving the early detection of psychiatric illnesses and their prevention," says Prof. Dr. Heike Tost, head of the Systems Neuroscience in Psychiatry (SNiP) working group at the CIMH in Mannheim.
DNA methylation of the FKBP5 gene determined
The researchers at the CIMH investigated the effects of the FKBP5 gene on the behavior and brain structure of 395 healthy test subjects. Blood samples were taken, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans were taken, and the participants answered questions about their thoughts and feelings on a study smartphone (Ecological Momentary Assessment) over a period of seven days.
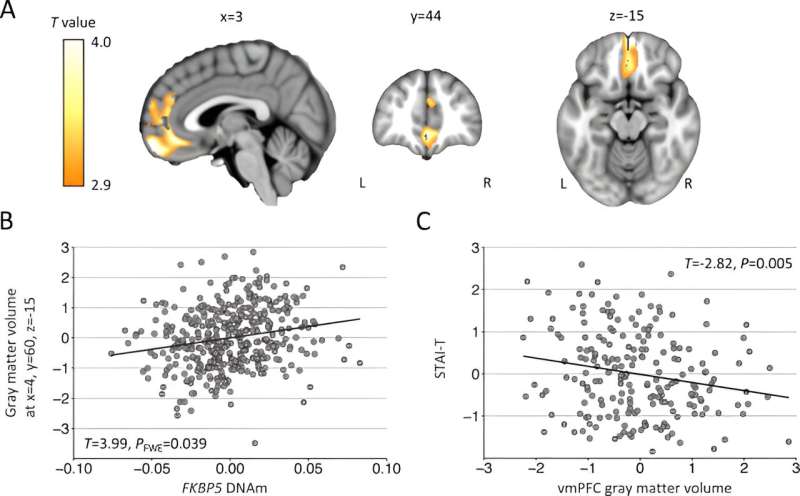
"In the blood samples, we first determined the DNA methylation of the FKBP5 gene. FKBP5 plays an important role in the molecular regulation of stress and is linked to the development of stress-related illnesses such as depression or post-traumatic stress disorder," explains Thomas L. Kremer, research associate in the SNiP working group and lead author of the study. DNA methylation is a regulatory process that controls the activity of genes.
It is not a genetic mutation but a modification of the genetic material that can be altered by environmental influences and affects its translation into proteins.
Brain volume changes in the prefrontal cortex
"Our key findings show that altered methylation of FKBP5 at the neurobiological level is associated with brain volume changes in the prefrontal cortex," says Kremer. The study also found that the functional change in the prefrontal cortex is linked to a structure deeper in the brain, the amygdala, and that people who had the less regulatory influence of the prefrontal cortex on the amygdala reacted more strongly to everyday stress.
"These findings are an important step towards understanding the biological basis of stress processing and psychiatric disorders," says Dr. Urs Braun, head of the Complex Systems in Psychiatry research group at the CIMH. "The long-term goal is to use this neurobiological understanding to develop innovative approaches for the personalized treatment of psychiatric patients."
More information: Thomas L. Kremer et al, Multimodal Associations of FKBP5 Methylation with Emotion-Regulatory Brain Circuits, Biological Psychiatry (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2024.03.003