This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
CMS121 mitigates aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction: Study
A new research paper titled "CMS121: a novel approach to mitigate aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction" has been published in Aging.
Modulated by differences in genetic and environmental factors, laboratory mice often show progressive weight gain, eventually leading to obesity and metabolic dyshomeostasis. The geroneuroprotector CMS121 has a positive effect on energy metabolism in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.
In this new study, researchers Alcir L. Dafre, Saadia Zahid, Jessica Jorge Probst, Antonio Currais, Jingting Yu, David Schubert, and Pamela Maher from Salk Institute for Biological Studies, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST) and Federal University of Santa Catarina investigated the potential of CMS121 to counteract the metabolic changes observed during the aging process of wild type mice.
"This comprehensive analysis aimed to further understand how CMS121 influences the metabolic landscape, paving the way for potential therapeutic applications beyond its established geroneuroprotective benefits," the researchers explain.
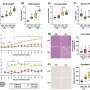
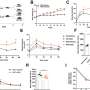
Control or CMS121-containing diets were supplied ad libitum for 6 months, and mice were sacrificed at the age of 7 months. Blood, adipose tissue, and liver were analyzed for glucose, lipids, and protein markers of energy metabolism. The CMS121 diet induced a 40% decrease in body weight gain and improved both glucose and lipid indexes. Lower levels of hepatic caspase 1, caspase 3, and NOX4 were observed with CMS121 indicating a lower liver inflammatory status.
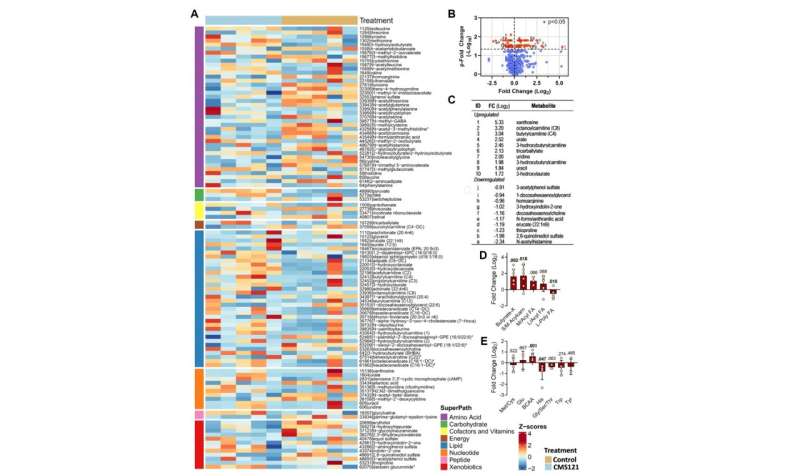
Adipose tissue from CMS121-treated mice showed increased levels of the transcription factors Nrf1 and TFAM, as well as markers of mitochondrial electron transport complexes, levels of GLUT4 and a higher resting metabolic rate. Metabolomic analysis revealed elevated plasma concentrations of short chain acylcarnitines and butyrate metabolites in mice treated with CMS121.
"The diminished de novo lipogenesis, which is associated with increased acetyl-CoA, acylcarnitine, and butyrate metabolite levels, could contribute to safeguarding not only the peripheral system but also the aging brain. By mimicking the effects of ketogenic diets, CMS121 holds promise for metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes, since these diets are hard to follow over the long term," the researchers conclude.
More information: Alcir L. Dafre et al, CMS121: a novel approach to mitigate aging-related obesity and metabolic dysfunction, Aging (2024). DOI: 10.18632/aging.205673