This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Researchers explore present and future treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma using immunotherapy
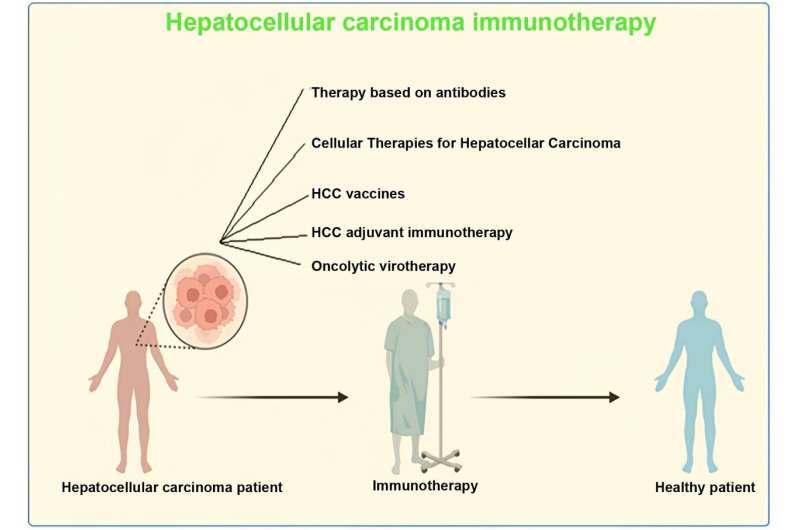
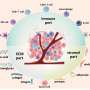
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a prevalent form of cancer, profoundly influences the progression and prognosis of the disease through immune response mechanisms. The tumor microenvironment plays a pivotal role in fostering immune suppression and maintaining self-tolerance, which are crucial in developing and refining immunotherapy approaches.
In a comprehensive review, researchers initially delve into the characteristics of the tumor microenvironment in HCC, elucidating the predominant immunosuppressive mechanisms at play and the biomarkers pivotal for tracking the disease progression and therapeutic response. Key biomarkers such as α-fetoprotein (AFP), used for diagnosis and monitoring, and emerging molecular markers are extensively discussed.
The work is published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
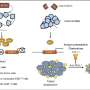
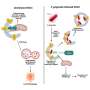
Central to the discussion is the transformative role of antibody-based therapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). These therapies, which include monoclonal antibodies targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), have revolutionized the approach to HCC treatment.
The researchers delve into the specifics of how these therapies reinvigorate the immune system's ability to recognize and attack tumor cells, discussing their application both as monotherapies and in combination with other targeted therapies. This segment underscores the significance of ICIs in managing advanced HCC, providing new avenues for first-line and subsequent treatments.
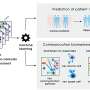
Additionally, the review explores various cellular immunotherapies such as T cell receptor (TCR) T cell therapy and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. The adaptability of these therapies to individual patient profiles illustrates the shift towards personalized medicine in oncology, aiming to optimize treatment efficacy based on unique tumor characteristics and patient immune profiles.
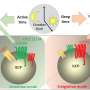
The potential of HCC vaccines, adjuvant immunotherapy, and oncolytic virotherapy is also thoroughly reviewed. Each of these therapeutic strategies exemplifies cutting-edge advances aiming to prime the immune system more effectively against HCC. The research team discuss the development stages of various vaccine types, their mechanisms of action, and the potential they hold in preventing recurrence and prolonging patient survival.
In conclusion, their detailed review highlights the dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape of HCC treatment. It reflects on the significant strides made in harnessing the immune system against HCC through innovative immunotherapies and sets the stage for future research that could unlock even more effective treatment modalities.
The continuous refinement of immunotherapeutic approaches promises to enhance outcomes for patients with HCC, transforming the prognosis of this challenging cancer.
More information: Hongbin Wei et al, Treatment Options for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Immunotherapy: Present and Future, Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (2024). DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00462