This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Study reveals key role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease
A research paper published in the journal Cell Metabolism by the team of Prof. Liu Qiang at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) reveals the critical role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease.
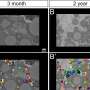
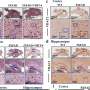
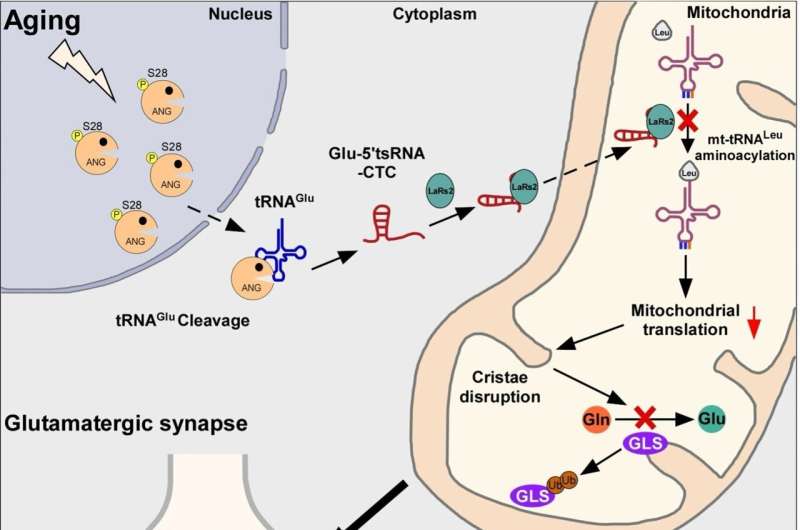
The study found age-dependent accumulation of Glu-5'tsRNA-CTC, a transfer-RNA-derived small RNA (tsRNA), derived from nuclear-encoded tRNAGlu in the mitochondria of glutaminergic neurons. This abnormal accumulation impairs mitochondrial protein translation and cristae structure, ultimately accelerating the pathological processes of brain aging and Alzheimer's disease.
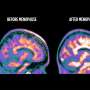
Brain aging is an inevitable natural process that leads to a decline in cognitive function. Alzheimer's disease, a neurodegenerative condition, is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly where cognitive impairment is a hallmark feature of Alzheimer's disease. Mitochondria provide energy to cells. Research has shown that mitochondrial dysfunction is closely associated with brain aging and Alzheimer's disease.
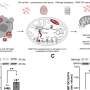
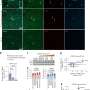
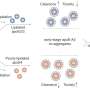
Mitochondrial Glu-5'tsRNA-CTC disrupts the binding of mt-tRNALeu and leucyl-tRNA synthetase 2 (LARS2), impairing mt-tRNALeu aminoacylation and mitochondrial-encoded protein translation. Defects in mitochondrial translation disrupt cristae architecture, resulting in impaired glutamine formation dependent on glutaminase (GLS) and reduced synaptic glutamate levels. Additionally, reducing Glu-5'tsRNA-CTC can protect the aging brain from age-related defects in mitochondrial cristae, glutamine metabolism, synaptic structure, and memory.
Liu and his team shed light on the crucial role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease, offering new insights for delaying cognitive decline. The researchers designed antisense oligonucleotides targeting these tRNA fragments and injected them into the brains of aged mice. This intervention significantly alleviated learning and memory deficits in the aged mice.
In addition to elucidating the physiological role of normal mitochondrial cristae ultrastructure in maintaining glutamate levels, this study also defined the pathological role of transfer RNAs in brain aging and age-related memory decline.
More information: Dingfeng Li et al, Aging-induced tRNAGlu-derived fragment impairs glutamate biosynthesis by targeting mitochondrial translation-dependent cristae organization, Cell Metabolism (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.02.011