This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Postexposure prophylaxis with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir does not cut COVID-19 infection
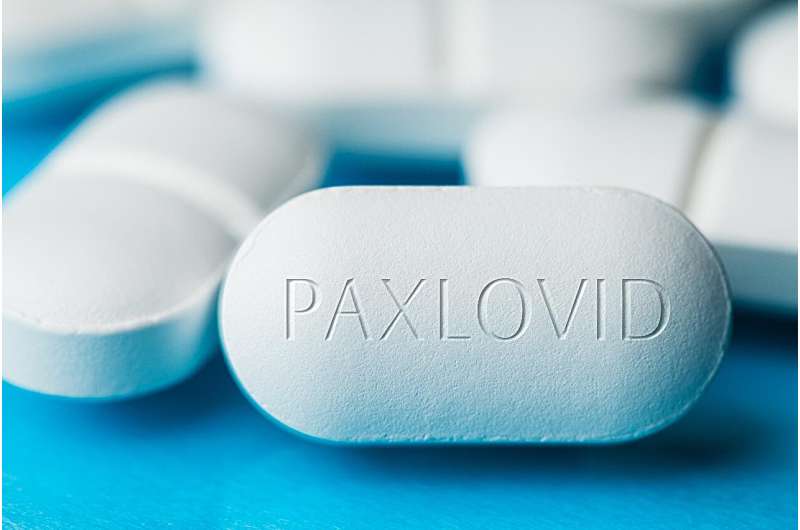

Postexposure prophylaxis with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for five or 10 days does not reduce the risk for symptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, according to a study published in the July 18 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Jennifer Hammond, Ph.D., from Pfizer in Collegeville, Pennsylvania, and colleagues conducted a phase 2 to 3 double-blind trial to examine the efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in asymptomatic adults who had been exposed to a household contact with COVID-19 within 96 hours before randomization and were rapid antigen test-negative for COVID-19. Participants were randomly assigned to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir every 12 hours for five days (921 participants) or for 10 days (917 participants) or to matching placebo for five or 10 days (898 participants).
The researchers found that symptomatic, confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection developed by day 14 in 2.6, 2.4, and 3.9% of participants in the five-day nirmatrelvir-ritonavir group, the 10-day nirmatrelvir-ritonavir group, and placebo group, respectively. The percentage of participants in whom symptomatic, confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection developed did not differ significantly for each nirmatrelvir-ritonavir group versus the placebo group, with risk reductions relative to placebo of 29.8 and 35.5% in the five- and 10-day nirmatrelvir-ritonavir groups, respectively. The trial groups had a similar incidence of adverse events.
"Among adult household contacts of symptomatic persons with confirmed COVID-19, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir given as postexposure prophylaxis for five or 10 days did not significantly reduce the risk of development of SARS-CoV-2 infection as compared with placebo," the authors write.
More information: Jennifer Hammond et al, Oral Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir as Postexposure Prophylaxis for Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309002
2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.