This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Study finds psychotherapy via texts can be just as effective
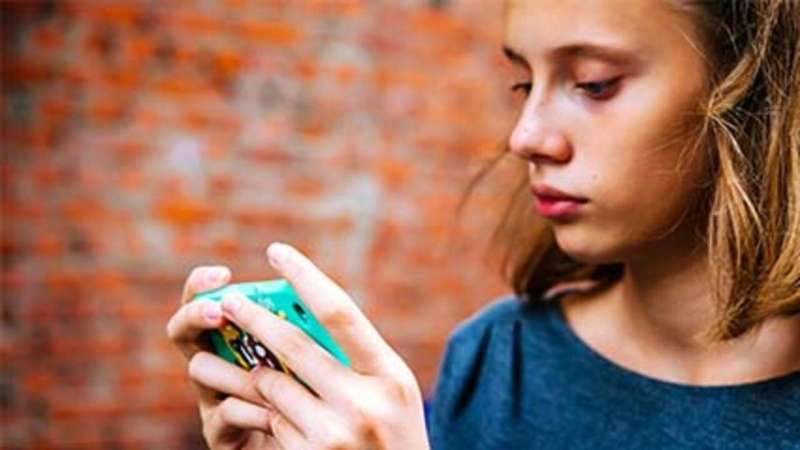

Folks with depression who got therapy via text or voice messages fared just as well as those who got weekly video-based telemedicine sessions with a therapist, a new trial has found.
The findings "suggest that psychotherapy delivered via text messages may be a viable alternative to face-to-face or videoconferencing delivery and may allow for more immediate on-demand care," in a time when it's often tough for people to access mental health care, the study authors wrote.
The trial was published July 19 in the journal Psychiatric Services.
The shutdown of traditional in-office services during the pandemic threw the spotlight on telemedicine as a means of delivering psychiatric care.
But are face-to-face video sessions the only effective way to deliver telemedicine?
In the new study, 215 adults with depression received 12 weeks of telemedicine care from a digital mental health care company called Talkspace.
Half of the patients received weekly standard videoconference sessions with a therapist for 30 to 45 minutes.
The other half received psychotherapy delivered via voice or text messages, where patients could interact with the therapist whenever and how often they wanted.
At the halfway point (six weeks), roughly the same number of patients— 28 patients receiving message-based therapy and 27 receiving videoconferencing therapy— showed "significant symptom improvements," according to a team led by Patricia Areán. She conducted the research while at the University of Washington.
"Significant" improvement in depression was defined as at least a 50% decline in scores on a standard questionnaire aimed at gauging mental health.
Folks who had failed to reach that goal by six weeks were switched to another six weeks of either weekly videoconferencing sessions plus message-based therapy, or monthly videoconferencing plus message-based therapy.
Overall, Areán's team found no real differences by the end of the 12-week study in outcomes for people who got videoconference therapy or therapy vis text/voice messaging. Patients in each group showed similar improvements in anxiety and overall functioning.
There was one major difference, however: Folks who were given the message-based therapy stuck with it an average of 7.8 weeks, much longer than the average of 4.9 weeks observed among the videoconferencing group.
All of the findings "are particularly important, given the challenges that many people have in accessing traditional psychotherapy," the researchers wrote in a journal news release.
Areán recently moved from her position at the University of Washington to become director of the National Institute of Mental Health's Division of Services and Intervention Research.
More information: Find out more about telemedicine in psychiatric care at the National Institute for Mental Health.
Patricia A. Areán et al, Randomized Trial of the Effectiveness of Videoconferencing-Based Versus Message-Based Psychotherapy on Depression, Psychiatric Services (2024). DOI: 10.1176/appi.ps.20230176
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.