This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
Social media can hamper teenagers figuring out who they want to be. Banning it until 16 is a good idea
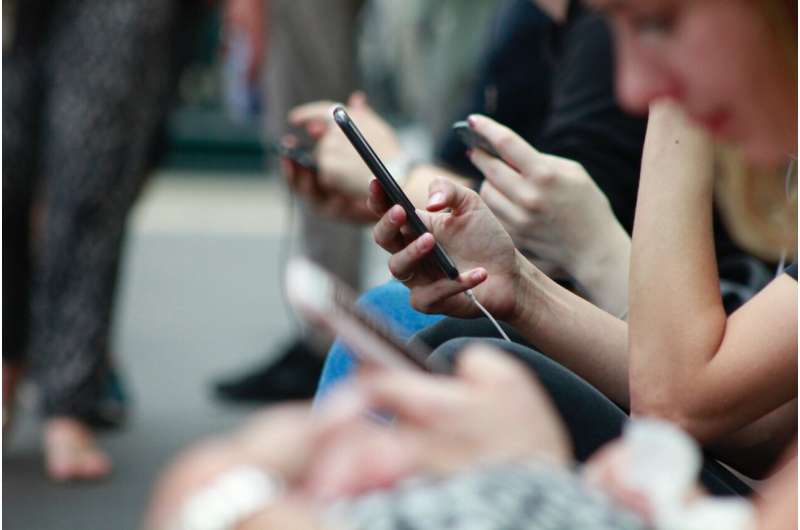

Over recent months, a number of politicians have supported calls to ban social media for children under 16 in Australia. Currently, kids under 13 are not allowed to use social media.
There's some research that suggests social media can be helpful for certain young people by, for example, connecting them with like-minded peers.
That said, there are a raft of reasons for this proposed change. The most compelling is evidence showing inappropriate screen time and social media use are linked to poor mental health in children and young people, including depression and anxiety.
Overuse or misuse of social media can damage many areas of psychological well-being. But, as an expert in adolescent development, I've been exploring one that's not often considered: identity development.
Identity development has long been regarded as the core psychological business of adolescence. You decide who you are, what you want to become, what underlying values you stand for and what you want out of life as you move toward adulthood. But might social media risk thwarting this process?
Developing an identity
Between the ages of about 11 and 15, the human brain becomes increasingly sensitive to attention and feedback from peers. The parts of the brain responsible for developing perspective, judgment, critical thinking and self-control will not fully mature until a person's early to mid 20s.
Teenagers have always compared themselves to others. They seek validation from peers as they explore their values, develop their personalities and seek to express themselves. But social media have provided a platform for adolescents—particularly those high in FOMO, or fear of missing out—to obsess over how they compare to many more people, including aptly named "influencers."
It can be difficult for a young person to develop a clear sense of self when they're constantly comparing themselves to and following others.
Similarly, young people are developing many of their opinions based on what they see on social media. An individual's tendency to conform to other people's opinions is sometimes called the "bandwagon effect."
While plenty of social media content can be harmless enough, social media—like the real world—are becoming increasingly political and polarized, with little tolerance for opposing ideas.
Some teens may find themselves latching onto ideologies fed to them via marketing algorithms. And we know young people can become radicalized through social media.
Living in the public sphere
Who are you? How do you see yourself? Are you the same person in public, in private, with friends, family or at work? Would you honestly admit some of your deepest feelings to your work colleague, friend, or even your partner? How about to yourself?
Harry Triandis, a psychology researcher who died in 2019, proposed differences between the "public" and "private" self that we all embody. Most people can relate to keeping their real opinions or values to themselves while in public or in an unknown group of people.
Once we are confident that our manner of speaking and underlying value systems won't be misconstrued, we start to reveal ourselves bit by bit. This process is the basis of forming friendships. And it's only in our most intimate relationships that we reveal ourselves fully.
Ask yourself, what embarrassing beliefs did you harbor across your lifespan, especially during your teenage years when your brain was still developing? Perhaps you held some stereotypes or biases that you now find embarrassing?
Your private self is the basis for quiet reflection, learning and changing your mind. But nowadays we see teens playing out their entire lives in the public sphere—essentially skipping this step.
Not only are they developing many of their opinions based on what they see on social media, but they often broadcast them online instantly. At a later time, they may be forced to defend these ideas.
In a 24/7 virtual world, there's less opportunity for today's teenager to critically think about what they are seeing online, self-reflect, explore and change their mind. There is little room to make mistakes, test boundaries, explore ideas and analyze information to forge their own identity.
These concerns are among the reasons many medical experts, parents and politicians alike want to limit access to social media for children.
While social media can continue to have detrimental effects for people older than 16, the earlier part of adolescence is an important time for the development of a young person's identity and self-worth.
Research has shown identity disturbance in adolescence—essentially an unstable sense of self—is a strong precursor to personality disorders in adulthood. We don't yet completely understand what life on social media does to developing identity, but it's vital we continue to explore this area.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()