This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
New definition of steatotic liver disease improves prediction of kidney disease
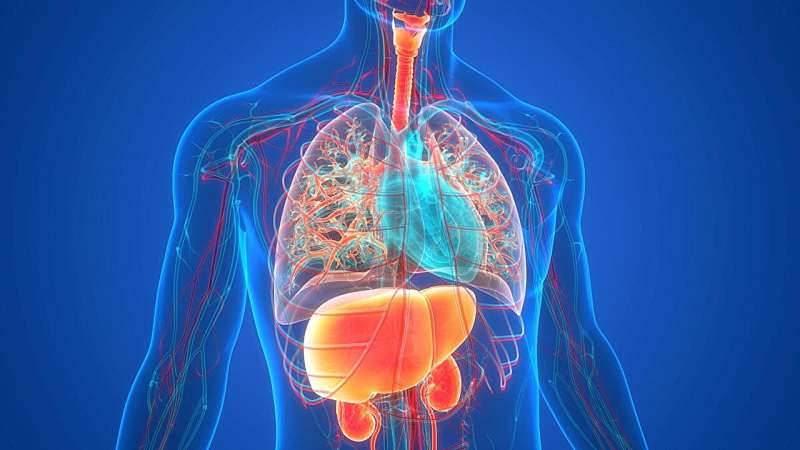
Using a new classification of steatotic liver disease (SLD) based on the presence of metabolic dysfunction and alcohol consumption, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) are significantly associated with the new onset of chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a study published online Aug. 7 in Hepatology Research.
Kazuma Mori, M.D., from the Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine in Japan, and colleagues investigated the effects of various SLDs on the development of CKD. The analysis included 12,138 Japanese individuals with annual health examinations that included abdominal ultrasonography during a 10-year period.
The researchers found that during follow-up, 16.2% of participants (17.2% of men; 14.2% of women) had new onset of CKD. When adjusting for age, sex, estimated glomerular filtration rate, current smoking habit, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, the risk for developing CKD was elevated in individuals with MASLD and those with ALD versus those with non-SLD; however, no association was seen for those with MASLD and increased alcohol intake.
Compared with those with non-SLD, participants with SLD without metabolic dysfunction had a significantly lower risk for CKD. The addition of the novel classification of SLDs into traditional risk factors for the development of CKD significantly improved discriminatory capacity.
"In clinical practice, it is possible to identify patients at high risk for CKD among those with SLD by classifying hepatic steatosis according to the new classification of SLDs," the study authors write.
More information: Kazuma Mori et al, Metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease (SLD) and alcohol‐associated liver disease, but not SLD without metabolic dysfunction, are independently associated with new onset of chronic kidney disease during a 10‐year follow‐up period, Hepatology Research (2024). DOI: 10.1111/hepr.14097
2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.