This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Autism spectrum disorders linked to neurotransmitter switching in the brain
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) involve mild to severe impairment of social, behavioral and communication abilities. These disorders can significantly impact performance at school, in employment and in other areas of life. However, researchers lack knowledge about how these disorders emerge at early stages of development.
University of California San Diego neurobiologists have found evidence of altered development of the nervous system in mouse models of autism spectrum disorders. They linked environmentally induced forms of ASD to changes in neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate with each other. They also discovered that manipulating these neurotransmitters at early stages of development can prevent the appearance of autistic-like behaviors.
The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"In seeking the root causes of autism spectrum disorder behaviors in the brain, we found an early change in neurotransmitters that is a good candidate to be the primary cause," said School of Biological Sciences Professor Nicholas Spitzer of the Department of Neurobiology and Kavli Institute for Brain and Mind. "Getting a handle on the early events that trigger ASD may allow development of new forms of intervention to prevent the appearance of these behaviors."
ASD diagnoses have been ramping up in recent years, but how these disorders manifest at the critical cellular and molecular levels has not been well understood.
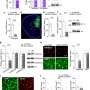
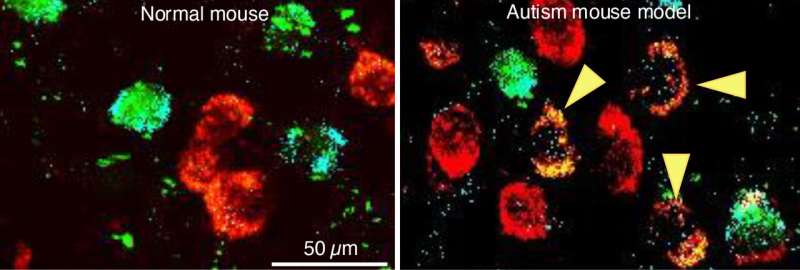
The study's lead author, Assistant Project Scientist Swetha Godavarthi, and colleagues investigated neurotransmitter expression in the medial prefrontal cortex, a brain area often affected in individuals diagnosed with ASD. They tested the hypothesis that changes in the type of neurotransmitter expressed by neurons in the prefrontal cortex could be responsible for a chemical imbalance that causes ASD-like behaviors.

Previous studies had shown an increase in the incidence of ASD in offspring when pregnant women had a heightened immune response or were exposed to certain drugs during the first trimester (environmental forms of ASD). The researchers reproduced ASD in mice by administering these environmental agents to mice in utero.
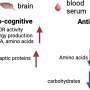
These agents caused the brief loss of the "GABA" neurotransmitter, which is inhibitory, and the gain of the "glutamate" neurotransmitter, which is excitatory, in neonatal mice. Although this GABA-to-glutamate transmitter switch reversed spontaneously after a few weeks, adult mice exhibited altered behaviors of repetitive grooming and diminished social interaction. Overriding this brief early transmitter switch in neonatal mice prevented the development of these autistic-like behaviors in adults.
"Driving expression of GABA in the neurons that have replaced GABA with glutamate prevents the appearance of stereotyped repetitive behavior and reduced social interaction," said Spitzer. "These findings demonstrate that changing electrical activity and inappropriately exciting neurons at early stages of development can alter the assembly of the nervous system."
Alterations in neurotransmitter expression at an early stage of development carry implications for other behavioral issues at later stages in life, since the rest of the nervous system is then built upon a platform of defective wiring, similar to a house constructed on an unstable foundation.
"Neurotransmitter switching can change the assembly of the nervous system and have a profound impact downstream," said Spitzer.
The researchers say the new results are consistent with other evidence that altering signaling in the nervous system during the early stages of development can later carry negative consequences as the brain matures.
Authors of the paper include Hui-quan Li, Marta Pratelli and Nicholas Spitzer.
More information: Swetha K. Godavarthi et al, Embryonic exposure to environmental factors drives transmitter switching in the neonatal mouse cortex causing autistic-like adult behavior, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2406928121. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2406928121