Last update:
Neuroscience news
Neuroscience
How astrocytes and perineuronal nets cooperate to sustain synaptic homeostasis
Synapses are small gaps between neurons through which signals are transmitted. This transmission of signals is what allows neurons to communicate and ultimately produce complex internal processes, such as thoughts and feelings, ...
17 hours ago
0
51
Medical research
Propofol shows promise in treating epilepsy by targeting HCN1 channels
The general anesthetic propofol may hold the keys to developing new treatment strategies for epilepsy and other neurological disorders, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Sweden's Linköping ...
14 hours ago
0
18
How adaptable to psychosocial stress is the teenage brain?
Mental illness often occurs for the first time during puberty and in young adulthood. This is because during adolescent brain development, a pronounced remodeling of cognitive networks takes place.
16 hours ago
0
15

Are cardiovascular risk factors linked to migraine?
Having high blood pressure, specifically high diastolic blood pressure, was linked to a slightly higher odds of ever having migraine in female participants, according to a new study published in the July 31, 2024, online ...
10 hours ago
0
0
Study uncovers unique brain plasticity in people born blind
A study led by Georgetown University neuroscientists reveals that the part of the brain that receives and processes visual information in sighted people develops a unique connectivity pattern in people born blind. They say ...
19 hours ago
0
48
Skin may hold key to neurodevelopmental disorder diagnoses
A genetic diagnostic method using a small sample of skin from the upper arm could identify rare neurodevelopmental disorders in a non-invasive way, according to researchers at the University of Adelaide.
16 hours ago
0
0

New high-resolution 3D maps show how the brain's blood vessels change with age
Healthy blood vessels matter for more than just heart health. Vascular well-being is critical for brain health and potentially in addressing age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders, like Alzheimer's ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
39

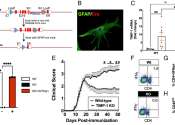
New work focuses on lack of TIMP-1 expression in the brains of MS patients
with a close family member living with multiple sclerosis Stephen J. Crocker, Ph.D., associate professor of neuroscience and immunology at UConn School of Medicine, takes his research personally.
Jul 30, 2024
0
37
Bilateral focused ultrasound shown to be safe, effective for patients with lingering or severe essential tremor
In a study published in JAMA Neurology co-authored by Vibhor Krishna, MD, associate professor of neurosurgery at the UNC School of Medicine, researchers found that a staged bilateral focused ultrasound treatment for essential ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
66

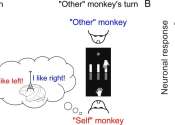
Neurons in the frontal cortex help macaque monkeys decode social interactions, study shows
By studying the brains of macaque monkeys during turn-taking exercises, researchers may be one step closer to understanding how individual neurons in the frontal cortex work together to analyze spatial locations of other ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
12
Study finds genetic variant among people who experience a rare recovery from ALS
Though it is exceedingly rare, some people diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) partially or fully recover from the lethal neurodegenerative disease.
Jul 30, 2024
0
2

Just a Minute: Avoiding 'brain fry' key to success on popular Radio 4 gameshow
Comedian Paul Merton and a Cardiff University academic have investigated why Radio 4 program "Just a Minute" is so challenging for players.
Jul 30, 2024
0
3

Spatial pattern of pathological changes in the brain can help identify dementia vulnerability early
Findings from a novel study in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, suggest that using a specialized diffusion weighted MRI scan to monitor the spatial pattern of individual cortical microstructural ...
Jul 30, 2024
0
0

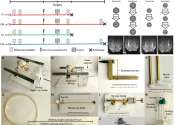
Brain cell grafts in monkeys jump-start human trial for new Parkinson's treatment
People with Parkinson's disease are receiving a new treatment in a clinical trial started after University of Wisconsin–Madison scientists demonstrated the safety and feasibility of the therapeutic delivery method in a ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
50
Advanced 'Parkinson's in a dish' model accelerates brain disease research
Researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, have developed a model that rapidly converts stem cells to brain cells with protein structures characteristic ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
19
Non-invasive device uses magnetoneurography to record involuntary nervous system
A research team led by UC San Diego has, for the first time, shown that a wearable, non-invasive device can measure activity in human cervical nerves in clinical settings.
Jul 29, 2024
0
38

New research suggests deaf children interact with parents like their hearing peers
A new study led by a Keele University research team has found that deaf toddlers fitted with cochlear implants interact with their parents just as well as their hearing peers.
Jul 29, 2024
0
63

First-ever effective therapy for rare, devastating neurodegenerative mitochondrial diseases
A new treatment could improve the lives of patients with mitochondrial diseases called POLG-related disorders, according to a unique clinical trial led by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center (RI-MUHC). ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
3

Inflammatory activity of rheumatoid arthritis linked to specific cognitive impairments
The inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
Jul 29, 2024
0
1

Teen alcohol exposure impairs behavioral flexibility and learning, shows persistent effects on brain chemistry
Rats with alcohol exposure in adolescence are less able as adults to adapt their behavior in changing circumstances, according to a study that highlights the possible brain mechanisms involved. The findings may help us better ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
1

ECT-induced seizure length tied to major depressive disorder remission
For patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), seizure duration of 60 to 69 seconds induced by electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is associated with the highest remission rates compared with seizure duration of less than ...
Jul 29, 2024
0
1

Video: The neuroscience of fencing
To make it to the Olympics, elite athletes spend countless hours preparing not only their bodies—but their brains, as well.
Jul 29, 2024
0
54

Central nervous system-associated macrophages could modulate post-stroke immune responses
An ischemic stroke is a type of stroke that occurs when a blood clot in an artery, also known as thrombus, or the progressive narrowing of arteries, blocks the blood and oxygen flowing to the brain. This process can cause ...

Building bridges between cells for brain health: Research finds microglia rescue neurons through tunneling nanotubes
The brain contains many cell types, from the prominent neurons to the lesser-known microglia. The latter are integral to the brain's immune system and play a crucial role as the brain's cleanup crew. A recent study conducted ...
Jul 26, 2024
0
92

A new therapeutic target offers a promising pathway for multiple sclerosis treatment
Researchers from Kyushu University have identified a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of advanced multiple sclerosis (MS), a potentially disabling condition associated with the central nervous system.
Jul 26, 2024
0
19