Light triggers death switch in cancer cells
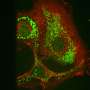
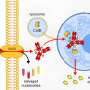
Researchers at Cardiff University have created a peptide (a small piece of protein), linked to a light-responsive dye, capable of switching 'on' death pathways in cancer cells. The peptide remains inactive until exposed to external light pulses which convert it into a cell death signal.
Complex mechanisms in healthy cells normally protect us from developing cancer. However, when the finely balanced networks of interactions between proteins that control such mechanisms are disturbed, uncontrolled cell growth can occur.
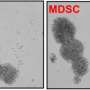
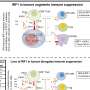
The Cardiff team has developed a peptide-switch to alter critical interactions in B-cell lymphoma cancer cells in a 'smart' and controlled way. This new pathway activation technology, called transient photoactivation, may enable scientists to identify cells normally resistant to chemotherapy leading to the development of more effective treatment strategies.
Professor Rudolf Allemann from Cardiff University's School of Chemistry, who led the research, said:
"Whilst killing cancer cells is a goal in itself, this is also proof of a wider principle. Directing therapeutic peptides to the precise location where they are required can be difficult, but activating peptides with light will allow us to precisely define the area where we wish a peptide to act.
"Our research demonstrates that we can control cellular processes with light, which has implications for research in biology and medicine, as our tools can be used to understand the inner workings of cells and to work out how to correct misfiring pathways that lead to disease.
"This work may eventually lead to photo-controlled drugs and tools to probe molecular interactions in intact cells and whole organisms with enormous consequences for biomedical research."