Potential new approaches to treating eye diseases
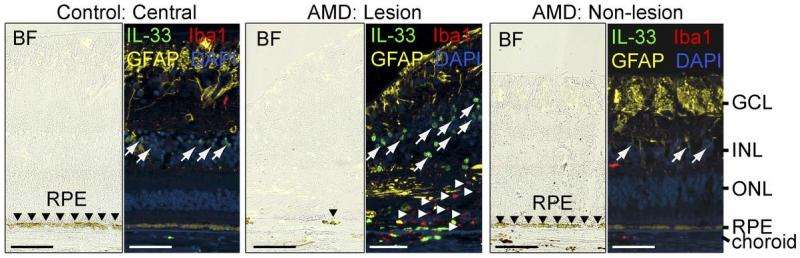
Potential new approaches to treating eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are described in a new study, "IL-33 amplifies an innate immune response in the degenerating retina," in the February Journal of Experimental Medicine.
AMD is a leading cause of vision impairment in old age, and is caused by the degeneration of cells in the retinal layer of the eye. Retinal cell death can be induced by phagocytic immune cells that infiltrate the tissue in response to injury or infection, but the molecular signals that trigger phagocyte invasion are largely unknown. A team of researchers led by Hongkang Xi and Menno van Lookeren Campagne, of the Department of Immunology at Genentech, Inc., in South San Francisco, Calif., discovered that a pro-inflammatory signaling protein, or cytokine, called IL-33, plays a key role in recruiting phagocytes to damaged retina and inducing retinal degeneration.
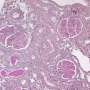
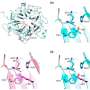
Working with rats and mice, Xi and colleagues found that specialized retinal cells called Müller glial cells release IL-33 in response to retinal injury. The cytokine then binds to its receptor on the surface of the Müller cells and induces the release of additional inflammatory proteins that attract phagocytes to the damaged retina. Blocking the IL-33 receptor inhibited this process and prevented injury-induced retinal degeneration.
The researchers also found that IL-33 levels are increased in the retinas of AMD patients, suggesting that the same pathway may occur in humans. Inhibiting IL-33 may therefore help treat AMD and other retinal degenerative diseases.
"This study for the first time shows increased expression of IL-33 in AMD and further demonstrates a role for glia-derived IL-33 in the accumulation of myeloid cells in the outer retina, loss of photoreceptors, and functional impairment of the retina in preclinical models of retina stress," the authors note.
More information: Hongkang Xi et al. IL-33 amplifies an innate immune response in the degenerating retina, The Journal of Experimental Medicine (2016). DOI: 10.1084/jem.20150894