Smokers who receive CT lung screening are more likely to quit

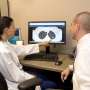
Smokers who undergo a CT scan of their lungs are more likely to quit than those who don't, concludes a trial led by Cardiff University.
The findings of the study, looking at the effect of CT screening on smokers at high-risk of developing lung cancer, dispute the belief that a negative screening result offers a 'licence to smoke' and reveal that engaging with lung screening can give smokers an opportunity to access smoking cessation support, at a time when they are likely to be receptive to offers of help.
Dr Kate Brain, Reader at Cardiff University's Division of Population Medicine, said: "Our trial shows that CT lung cancer screening offers a teachable moment for smoking cessation among high-risk groups in the UK. We now need evidence about the best ways of integrating lung cancer screening with stop-smoking support, so that services are designed to deliver the maximum health benefits for current and future generations."
The trial, led by researchers at Cardiff University working with the University of Liverpool, King's College London and Queen Mary University, involved 4,055 participants aged 50-75 years who were randomised either to a group who underwent low-dose CT screening for early detection of lung cancer, or to a control group who did not undergo screening.
Of the smokers who took part in the screening, 10 percent had successfully quit after two weeks, and 15 percent had quit at two years – both higher than rates in the control group.
The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) pilot trial is the first to assess the feasibility, cost-effectiveness and behavioural impact of lung cancer screening, using a single low-dose CT screen on a high-risk population in the UK.
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious types of cancer and has the highest mortality of all cancers in the UK. Around 44,500 people are diagnosed with the condition every year in the UK.
The UKLS pilot trial was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment programme.
The full scientific publication 'Impact of low-dose CT screening on smoking cessation among high-risk participants in the UK Lung Cancer Screening Trial' is published in Thorax.
More information: Kate Brain et al. Impact of low-dose CT screening on smoking cessation among high-risk participants in the UK Lung Cancer Screening Trial, Thorax (2017). DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209690