TXNIP blocks autophagic flux, causes alpha-synuclein accumulation
(HealthDay)—Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) blocks autophagic flux and induces expression of α-synuclein accumulation via inhibition of ATP13A2, according to a study published online July 29 in CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.
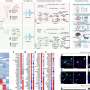
Cun-Jin Su, from the Hospital of Soochow University in Suzhou, China, and colleagues examined the effects of TXNIP on autophagic flux and α-synuclein accumulation by Western blot in HEK293 cells, which had been transfected with TXNIP plasmid.
The researchers found that TXNIP induced expression of LC3-II, but failed to degrade the autophagy substrate p62. TXNIP also aggravated accumulation of α-synuclein. TXNIP inhibited the expression of the lysosomal membrane protein ATP13A2; overexpression of ATP13A2 attenuated the TXNIP-linked impairment of autophagic flux and α-synuclein accumulation. In the substantia nigra, overexpression of TXNIP resulted in loss of dopaminergic neurons.
"Our data suggested that TXNIP blocked autophagic flux and induced α-synuclein accumulation through inhibition of ATP13A2, indicating TXNIP was a disease-causing protein in Parkinson's disease," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.