New procedure enables cultivation of human brain sections in the petri dish
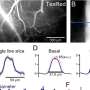
Researchers at the University of Tübingen have become the first to keep human brain tissue alive outside the body for several weeks. The researchers, headed by Dr. Niklas Schwarz, Dr. Henner Koch and Dr. Thomas Wuttke at the Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research, published their findings in the latest edition of Scientific Reports.
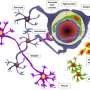
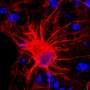
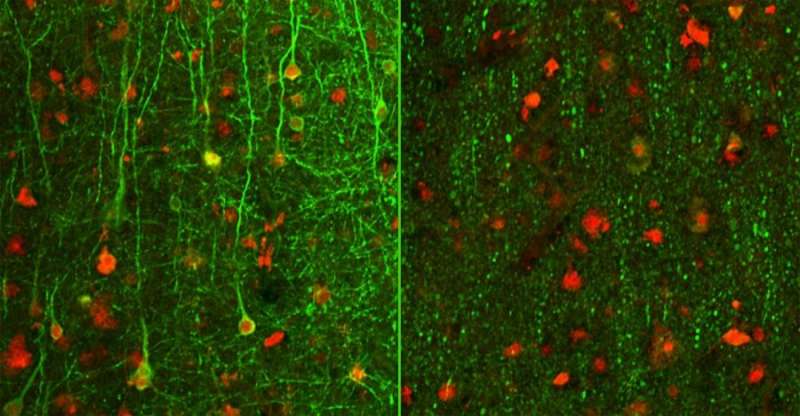
The reason for this success is apparently the use of human cerebrospinal fluid to cultivate the tissue in the laboratory. The tissue cultures were in good shape and able to function even after three weeks in a petri dish. Previous attempts to keep brain sections alive used a standard culture solution – which does not work well for human tissue. That is one reason why researchers often fall back on animal experiments. The scientists say the new procedure expands the range of options open for carrying out tests on human brain cells. For instance, it simplifies tests to find out whether brain tissue can tolerate new drugs.
"The human brain appears to have a very low tolerance for cultivation outside the human body," says Dr. Henner Koch, who lead the study. It is not yet clear which substances in human cerebrospinal fluid are key to the survival of nerve tissue. That will be a goal for future analyses.
But it is clear that the new method answers some of the questions about human brain tissue which used to require animal experiments. In the future, researchers will be able to test the effects of new pharmaceuticals on human brain tissue using cell cultures in a petri dish. And the results of animal experiments are not always fully applicable to humans – leaving a margin of risk for voluntary subjects in the testing of new drugs.
The new technique will also make it easier to research genetic mutations associated with human nervous system disorders. "The method enables us to introduce a mutation into the brain cells and to investigate its effect on the tissue as a whole," says lead author Dr. Niklas Schwarz. "Even though many neurological disorders can be studied using animal models – it is often uncertain that the results can be transposed to human brain cells." The Tübingen researchers hope that their process will reduce the number on animals used in experiments.
Yet there will not be mass experiments on human brain sections in the future. The researchers can only use tissue which has been removed as part of necessary brain surgery. That may be the case when epilepsy can no longer be treated using drugs and the damaged area of the brain has to be removed. "Of course, we only use material from patients who have consented to its scientific use in writing," says neurosurgeon and co-author, Dr. Thomas Wuttke.
More information: Niklas Schwarz et al. Human Cerebrospinal fluid promotes long-term neuronal viability and network function in human neocortical organotypic brain slice cultures, Scientific Reports (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12527-9