Q&A: Infectious diseases expert talks vaccines and COVID-19
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues its spread, harming and hampering lives and economies, one thing is clear: we need a vaccine.
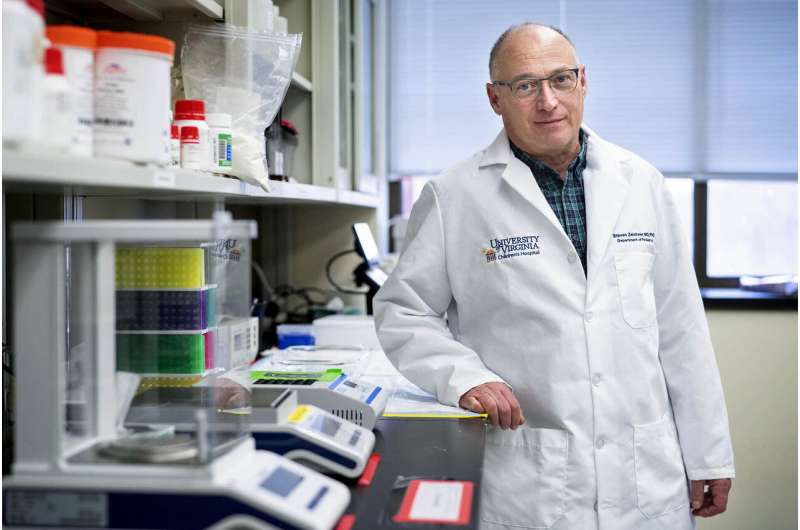
Dr. Steven Zeichner, a University of Virginia infectious diseases specialist and researcher, is responding to that challenge. He is using existing technologies and techniques to develop a unique vaccine-making method that he hopes will not only rapidly produce a safe and effective vaccine, but one that is low-cost and highly manufacturable.
Here, he discusses vaccines generally, and his particular approach to vaccine development.
Q. When do you think an approved COVID-19 vaccine will become available?
A. That's still an open question. A year or so from now would be wonderful, but that would be very fast for a new vaccine because there are a lot of things that can go wrong in development. I would be delighted to see it happen.
It would need to first be widely tested in Phase III clinical trials, and then, if proven safe and effective, would have to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration. It then would have to be produced in sufficient quantities to elicit immunity in a significant fraction of the population.
Q. What are the steps involved in creating a vaccine?
A. First, we need a vaccine that can elicit an appropriate immune response in an animal.
If that works, then we do a Phase I study in a small number of people to see if they, too, demonstrate immunity with no evidence of a safety problem.
Then a Phase II study is conducted on a larger number of people to see if there's more evidence of safety and efficacy.
Next, a large Phase III study is needed, where you immunize many, many people and see if the vaccine actually protects them from getting the infection. If so, that would lead to drug approval and production for the general population.

It's a long process.
In a pandemic situation, there are groups trying to accelerate this by combining phases, which is a reasonable way to go when faced with a crisis. But until we get the Phase III data, we don't actually know whether the vaccine is going to be safe and protective, with no adverse effects.
Q. Once a vaccine is developed and approved, can we produce enough doses for everyone?
A. That's another major open question, because even the vaccines that are in the most advanced stages of development—some already accelerated to Phase III—may still require a year to produce a billion doses. With many vaccines, you need more than one dose to complete a course of vaccination.
So depending on how many doses are needed for an effective immune response—perhaps two or three per individual—a billion doses might immunize the United States, but the U.S. is only about 5% of the global population. A billion doses are not nearly enough to immunize everybody in the world.
Q. What about affordability? Will it come down to how wealthy you are and what nation you live in?
A. My personal ethical view is that everyone should be able to get a vaccine. But who's going to pay for that—individuals, health insurers, governments? Some vaccines cost several hundred dollars for a full course, making them out of reach for many people in the U.S. and many more around the world. So, a vaccine costing hundreds of dollars is worthless for most people.
Q. Considering the hurdles involved in developing, testing, mass-producing and distributing a COVID-19 vaccine, is it possible that so-called herd immunity could happen first, providing a certain amount of large-scale population protection?
A. Absent a vaccine, I think this virus is going to be with us a long time. Epidemiologists suggest it might take 50% to 60% of the population becoming immune to stop the widespread proliferation of disease in the population. That could happen, but then many people would get sick and die along the way.
We think now that when you're infected with the virus, you have some level of protective immunity. But we still don't know that for sure, and we don't know how durable the immunity is.