New clinical practice guideline on fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) to help guide asthma treatment

In its latest clinical practice guideline on evaluation and treatment of asthma, an American Thoracic Society expert guidelines panel has addressed the use of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) to guide the treatment of asthma. The guideline was published online in the Nov. 15 issue of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
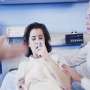
The FeNO test is a point of care test that measures the level of nitric oxide gas in an exhaled sample of a patient's breath. This sample is collected by having the patient breathe slowly and steadily into a mouthpiece that is attached to a machine that performs the measurement.
The practice guideline is designed to provide guidance to clinicians who care for adults and children four years and older with asthma, including adult and pediatric pulmonologists, adult and pediatric allergists, internists, pediatricians, family medicine specialists, and other health care professionals who care for individuals with asthma.
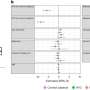
The one question the expert panel addressed was: Should patients with asthma in whom treatment is being considered undergo FeNO testing?
Following the initial development of FeNO as a test in 2011, the American Thoracic Society developed a clinical practice guideline for the interpretation of FeNO in adults and in children over four years of age. Since the development of this initial guideline, several well-conducted studies divided FeNO values into more narrowly defined ranges and confirmed the value of this test for multiple asthma outcome measurements.
A number of key questions about FeNO remained, but based on several systematic reviews, the expert panel was asked to identify and address the most critical question that impacts patient care. The question that was chosen assesses the utility of the FeNO test in management of individuals in whom treatment is being contemplated.
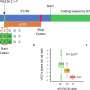
Using the thorough, evidence-based Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) framework, the expert panel made the following recommendation, which addressed the question above.
Recommendation: "In patients with asthma in whom treatment is being considered, we suggest the use of FeNO in addition to usual care over usual care alone (conditional recommendation, low confidence in estimates of effect)."
"While our task was to review whether FeNO testing be performed when treatment is being considered, the studies being evaluated as well as the interpretation of results via our methodology suggest that any patient with asthma may be eligible for the measurement of FeNO in decision making regarding therapy," noted guideline co-chairs Sumita B. Khatri, MD, MA and Teal S. Hallstrand, MD, MPH. "As rigorous as our evaluation of the single question we were asked to investigate was, it should be noted that this guideline does not address the question of FeNO to establish the diagnosis of asthma or the utility of FeNO in monitoring asthma. We believe these issues that were identified by the panel as being important should be addressed in the future in a systematic manner."
More information: Sumita B. Khatri et al, Use of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide to Guide the Treatment of Asthma: An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine (2021). DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2093ST
The ATS has published more than 20 clinical practice guidelines on various conditions, ranging from allergy and asthma to TB and other pulmonary infections.