SARS-CoV-2 infection could cause alterations in pain perception
Physicians from the Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) have observed a surprising phenomenon during the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: Some patients with cancer-related pain have experiences a significant decrease or even disappearance of pain perception during the acute phase of infection.
This case study would confirm the hypotheses made by the same team about the absence of the perception of shortness of breath in a large proportion of patients with severe COVID 19. Although more studies are needed to confirm these observations, these cases suggest that infection with SARS-CoV-2 could induce atypical symptoms, possibly through nervous system dysfunction. A case series that can be read in the international scientific journal Pain.
Until now, several factors related to COVID-19 have been widely accepted as worsening chronic pain. A multidisciplinary team from HUG, led by Dr. Lisa Hentsch, M.D. senior resident at the Division of Palliative Medicine, and Dr. Matteo Coen, M.D., M.D.-Ph.D. senior resident at the Division of Internal Medicine, surrounded by experts in internal medicine and palliative, neurology, radiology and pathology have revealed for the first time an unexpected phenomenon: a significant, albeit transient, reduction of pain in three oncological patients suffering from severe COVID-19.
COVID-19 could reduce the perception of pain
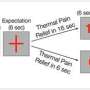
The patients, three men aged 67 to 84 years old, were followed by the outpatient consultation of palliative care for severe oncological pain, refractory to opioid treatment. Hospitalized at the HUG due to COVID-19, all patients observed a decrease or even a disappearance of their pain soon after infection. The recovery from COVID-19 was also associated with a gradual return of pain in one of the patients. At the moment, this phenomenon remains unexplained, but the team is making a few assumptions.
Insular cortex dysfunction?
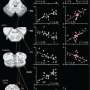
In a previous article published in the Journal of Medical Virology, the authors discussed about another very common phenomenon in patients suffering from severe COVID-19: the absence of dyspnea (struggle to breath) despite lower than normal oxygen levels (commonly known as "happy hypoxemia"). Both pain and dyspnea are subjective experiences that result from complex mechanisms in which the insular cortex plays an essential role.
The insular cortex, or insula, is a part of the cerebral cortex, buried deep in the folds of the cortex. It plays a role in different body functions. In particular, the insula is responsible for the "awareness" of internal perceptions (interoception), an essential element for the construction of experiences such as pain and dyspnea.
A dysfunction of this area, due to a direct effect of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or as a consequence of the "inflammatory storm" common in severe COVID-19, could indeed be responsible for a blunted, or even absent, perception of pain and dyspnea. An alternative hypothesis could be a direct, SARS-CoV-2-induced dysfunction in the peripheral nervous system. Capable of interfering with the transmission of the nervous message responsible for pain and labored breathing perception.
Further studies are needed to confirm these observations and validate these hypotheses. Nevertheless, these observations could shed new light on the mechanisms responsible for pain perception and eventually open up new avenues of research and therapy.
These early findings on temporary pain reduction are the subject of an article published in the prestigious international scientific journal Pain, the leading journal devoted to the study of pain.
More information: Lisa Hentsch et al, Decrease in pain perception during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, Pain (2021). DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002512