Study shows need for painkiller caution to prevent kidney damage
Taking too much ibuprofen or similar painkillers can damage kidneys, but a recent study has revealed some people at high risk are still being prescribed them.
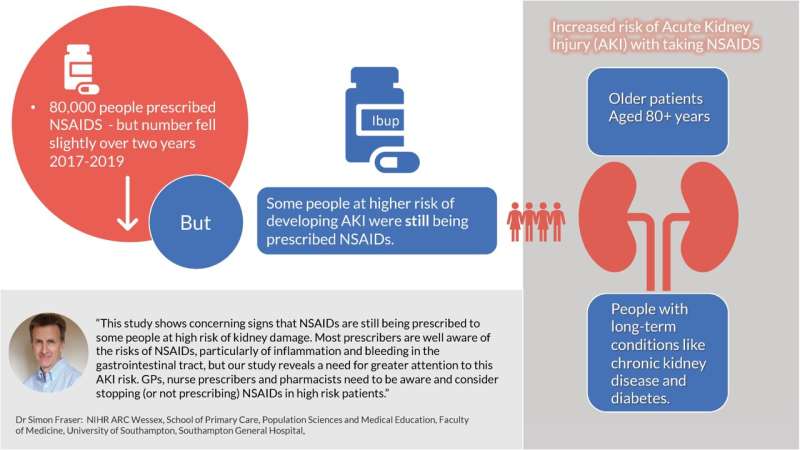
Research has found that prescriptions of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduced over the two years before the pandemic. However, they were still being given to some people at high risk of kidney damage.
The study was led by Dr. Simon Fraser, Associate Professor of Public Health at the University of Southampton.
Avoiding kidney damage
NSAIDs are commonly prescribed to treat pain and inflammation. However, they can cause serious complications such as acute kidney injury (AKI).
This is where a person's kidneys suddenly stop working properly. It can range from minor loss of kidney function to complete kidney failure.
Without quick treatment, abnormal levels of salts and chemicals can build up in the body. This affects the other organs' ability to work properly.
If the kidneys shut down completely, the person may need dialysis or a kidney transplant. It can be fatal.
Prescriptions in those at higher risk
The researchers analyzed data on 702,265 adults from a large primary care database in Hampshire to investigate NSAID prescriptions over two years.
Their results, published in BJGP Open, suggested a general decrease in NSAID prescriptions. This included in those at higher risk of developing AKI.
However, it revealed that some people at higher risk of developing AKI were still being prescribed NSAIDs. These included older patients and those with long-term conditions like chronic kidney disease and diabetes.
Dr. Fraser said: "This study shows concerning signs that NSAIDs are still being prescribed to some people at high risk of kidney damage. Most prescribers are well aware of the risks of NSAIDs, particularly of inflammation and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, but our study reveals a need for greater attention to this AKI risk. GPs, nurse prescribers and pharmacists need to be aware and consider stopping (or not prescribing) NSAIDs in high-risk patients."
More information: Sharon X Lin et al, Characterising risk of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-related acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study, BJGP Open (2021). DOI: 10.3399/BJGPO.2021.0208