Gene therapy shows promise in treating neuropathy from spinal cord injuries
An international team of researchers, led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, report that a gene therapy that inhibits targeted nerve cell signaling effectively reduced neuropathic pain with no detectable side effects in mice with spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries.
The findings, published in the May 5, 2022 online issue of Molecular Therapy, represent a potential new treatment approach for a condition that may affect more than half of patients who suffer spinal cord injuries. Neuropathy involves damage or dysfunction in nerves elsewhere in the body, typically resulting in chronic or debilitating numbness, tingling, muscle weakness and pain.
There are no singularly effective remedies for neuropathy. Pharmaceutical therapies, for example, often require complex, continuous delivery of drugs and are associated with undesirable side effects, such as sedation and motor weakness. Opioids can be effective, but can also lead to increased tolerance and risk of misuse or abuse.
Because physicians and researchers are able to pinpoint the precise location of a spinal cord injury and origin of neuropathic pain, there has been much effort to develop treatments that selectively target impaired or damaged neurons in the affected spinal segments.
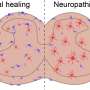
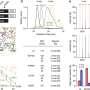
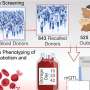
In recent years, gene therapy has proven an increasingly attractive possibility. In the latest study, researchers injected a harmless adeno-associated virus carrying a pair of transgenes that encode for gamma-aminobutyric acid or GABA into mice with sciatic nerve injuries and consequential neuropathic pain. GABA is a neurotransmitter that blocks impulses between nerve cells; in this case, pain signals.
The delivery and expression of the transgenes—GAD65 and VGAT—was restricted to the area of sciatic nerve injury in the mice, and as a result, there were no detectable side effects, such as motor weakness or loss of normal sensation. The production of GABA by the transgenes resulted in measurable inhibition of pain-signaling neurons in the mice, which persisted for at least 2.5 months after treatment.
"One of the prerequisites of a clinically acceptable antinociceptive (pain-blocking) therapy is minimal or no side effects like muscle weakness, general sedation or development of tolerance for the treatment," said senior author Martin Marsala, MD, professor in the Department of Anesthesiology in the UC San Diego School of Medicine.
"A single treatment invention that provides long-lasting therapeutic effect is also highly desirable. These finding suggest a path forward on both."
More information: Takahiro Tadokoro et al, Precision spinal gene delivery-induced functional switch in nociceptive neurons reverses neuropathic pain., Molecular Therapy (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.04.023